1

ABA | Abscisic acid (C1) (for immunolocalization)
AS09 446 | Clonality: Polyclonal | Host: Rabbit | Reactivity: Arabidopsis thaliana, Eucalyptus globulus, Pinus radiata
- Product Info
-
Immunogen: BSA-conjugated abscisic acid (C1) via C1 carboxyl group
Host: Rabbit Clonality: Polyclonal Purity: Total IgG. Protein G purified in PBS with 50 % glycerol. Format: Liquid Quantity: 200 �g Storage: Store lyophilized/reconstituted at -20�C; once reconstituted make aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Please remember to spin the tubes briefly prior to opening them to avoid any losses that might occur from material adhering to the cap or sides of the tube. Tested applications: Immunofluorescence (IF), Immunolocalization (IL) Recommended dilution: The optimal working dilution should be determined by the investigator - Reactivity
-
Confirmed reactivity: Abscisic acid (C1) in Arabidopsis thaliana, Eucalyptus globulus, Petunia hybrida L., Pinus radiata, Populus trichocarpa Predicted reactivity: Abscisic acid (C1) Not reactive in: No confirmed exceptions from predicted reactivity are currently known - Application Examples
-
Application examples: 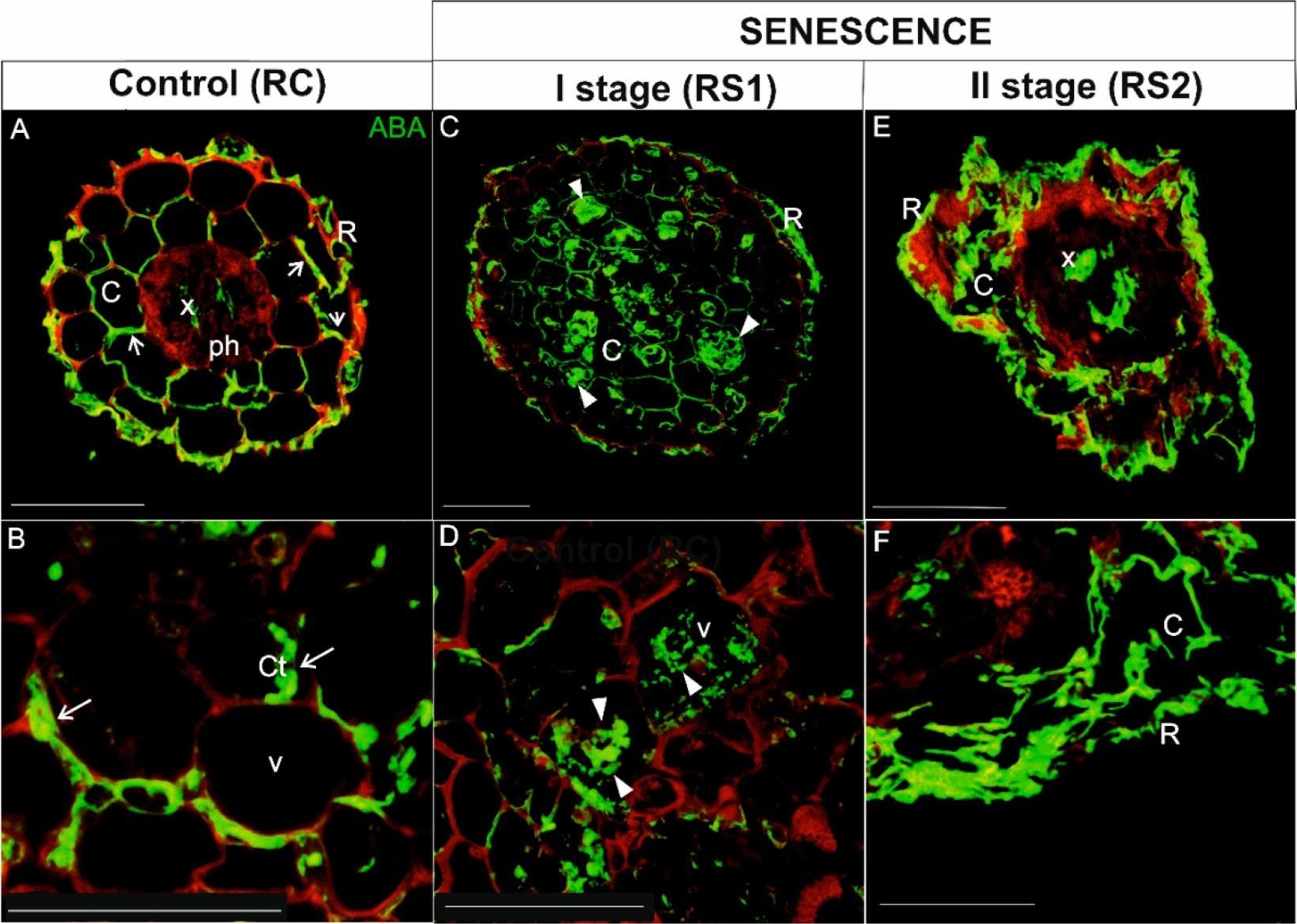
Reactant: Populus trichocarpa (Black cottonwood)
Application: Immunohistochemistry-immunofluorescence
Pudmed ID: 32192046
Journal: Int J Mol Sci
Figure Number: 7A,B,C,D,E,F
Published Date: 2020-03-17
First Author: Wojciechowska, N., Wilmowicz, E., et al.
Impact Factor: 5.542
Open PublicationImmunolocalization of ABA (green fluorescence) during senescence process of fine, absorptive roots. (A,B) Root control (RC); (C,D) The first stage of root senescence (RS1); (E,F) The second stage of root senescence (RS2). Autofluorescence (red) of the cell wall was registered in order to visualize the cell/organ shape. Abbreviations: R, rhizodermis; C, parenchyma cortex cells; Ct, cytoplasm; Ph, phloem, X, xylem. Scale bars = 50 �m.
Reactant: Populus trichocarpa (Black cottonwood)
Application: Immunohistochemistry-immunofluorescence
Pudmed ID: 32192046
Journal: Int J Mol Sci
Figure Number: 8A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H,I
Published Date: 2020-03-17
First Author: Wojciechowska, N., Wilmowicz, E., et al.
Impact Factor: 5.542
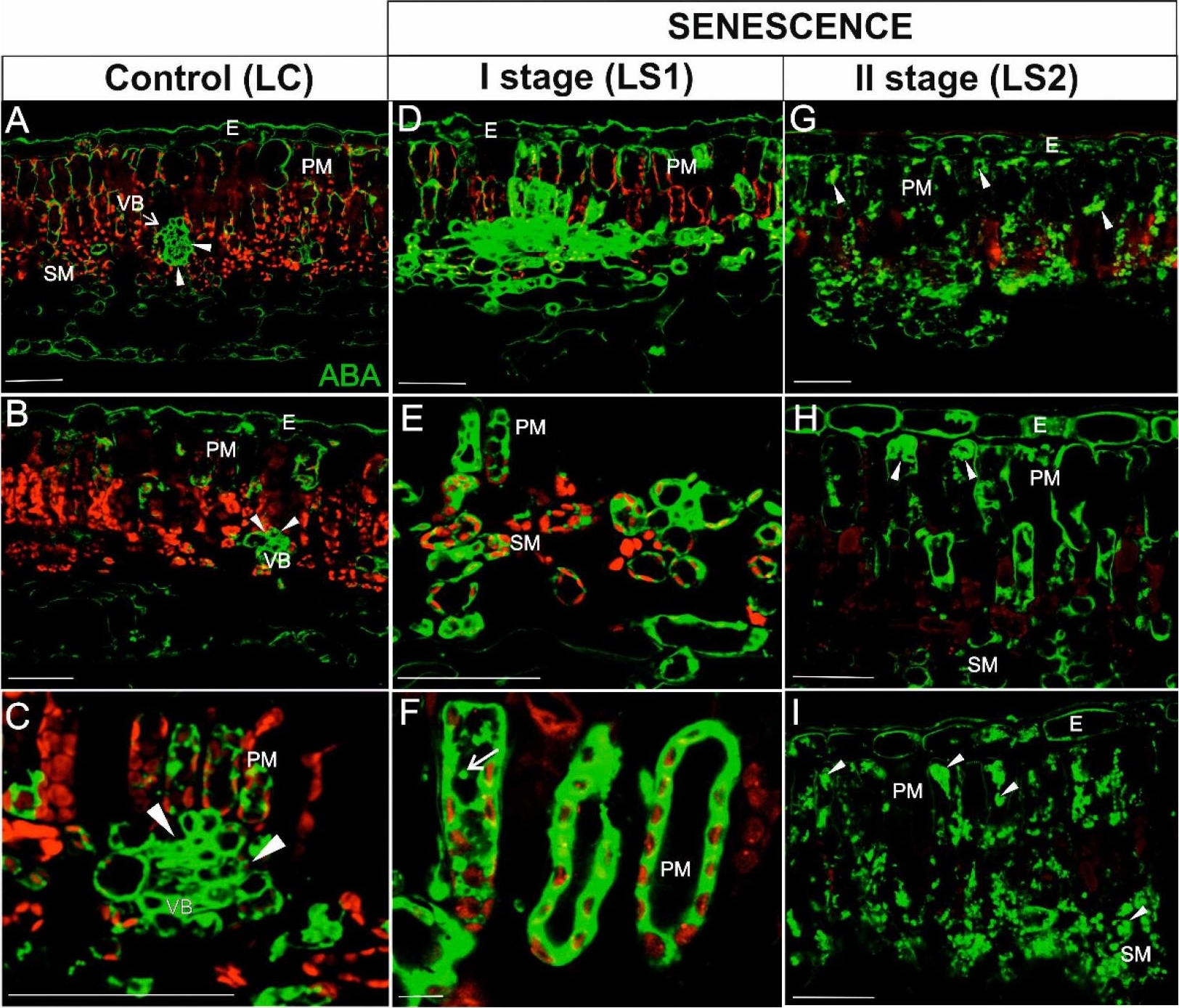
Open PublicationImmunodetection of ABA (green fluorescence) and red autofluorescence of chlorophyll during leaf senescence. (A–C) Leaves control (LC); (D–F) The first stage of leaf senescence (LS1); (G–I), The second stage of leaf senescence (LS2). Abbreviations: VB, vascular bundle; PM, palisade mesophyll; SM, spongy mesophyll; E – epidermis. Scale bars = 50 �m.
- Additional Information
-
Additional information: ABA | Abscisic acid (C1) (for immunolocalization) Additional information (application): The antibody will recognize either the ABA conjugated to glucose ester (ABA-GE) or the ABA precursor: abscisic acid aldehyde, ABA aldehyde is however not usually present in plant tissue similarly to ABA alcohol which is also reactive, The antibodies will predominantly recognize only ABA and its glucosylester - Background
-
Background: Abscisic acid (ABA) is a plant hormone involved in different physiological responses as stimulation of the closure of stomata (water stress brings about an increase in ABA synthesis), iInhibition of shoot growth, and many others. ABA shown to have both inhibitory as well as many promoting functions.
- Product Citations
-
Selected references: Wojciechowska et al. (2020). Abscisic Acid and Jasmonate Metabolisms Are Jointly Regulated During Senescence in Roots and Leaves of Populus trichocarpa. Int J Mol Sci , 21 (6)
Dinis et al. (2018). Kaolin modulates ABA and IAA dynamics and physiology of grapevine under Mediterranean summer stress. J Plant Physiol. 2018 Jan;220:181-192. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2017.11.007.
Kovaleva et al. (2017). ABA and IAA control microsporogenesis in Petunia hybrida L. Protoplasma. 2017 Nov 13. doi: 10.1007/s00709-017-1185-x.
Escandón et al. (2016). Integrated physiological and hormonal profile of heat-induced thermotolerance in Pinus radiata. Tree Physiol. 2016 Jan;36(1):63-77. doi: 10.1093/treephys/tpv127. Epub 2016 Jan 12.
Ondzighi-Assoume et al. (2016). Environmental Nitrate Stimulates Root Tip Abscisic Acid Accumulation via Release from Inactive Stores. Plant Cell. 2016 Feb 17. pii: TPC2015-00946-RA.
Jesus et al. (2015). Salicylic acid application modulates physiological and hormonal changes in Eucalyptus globulus under water deficit. Environ and Exp Botany, Volume 118, October 2015, Pages 56–66.
Lacuesta et al. (2013). Immunolocalization of IAA and ABA in roots and needles of radiata pine (Pinus radiata) during drought and rewatering. Tree Physiol. May;33(5):537-49.
- Reviews:
-
This product doesn't have any reviews.
Accessories

AS06 193 | Clonality: Polyclonal | Host: Rabbit | Reactivity: IAA | Indole 3 acetic acid
Sold out. Other antibodies to IAA can be found here.


