1
Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H&L), DyLight® 488 conjugated
AS09 633 | Clonality: Polyclonal | Host: Goat | Reactivity: Rabbit IgG (H&L)
- Product Info
-
Immunogen: Purified Rabbit IgG, whole molecule
Host: Goat Clonality: Polyclonal Purity: Immunogen affinity purified goat IgG. Format: Lyophilized Quantity: 1 mg Reconstitution: For reconstitution add 1.1 ml of sterile water. Let it stand 30 minutes at room temperature to dissolve. Prepare fresh working dilutions daily Storage: Store lyophilized material at 2-8°C. Product is stable for 4 weeks at 2-8°C after rehydration. For long time storage after reconstitution, dilute the antibody solution with glycerol to a final concentration of 50% glycerol and store as liquid at -20°C, to prevent loss of enzymatic activity. For example, if you have reconstituted 1 mg of antibody in 1.1 ml of sterile water add 1.1 ml of glycerol. Such solution will not freeze in -20°C, If you are using a 1:5000 dilution prior to diluting with glycerol, then you would need to use a 1:2500 dilution after adding glycerol. Prepare working dilution prior to use and then discard. Be sure to mix well but without foaming. Tested applications: Immunocytochemistry (ICC), Immunohistochemistry (IHC), Immunofluorescence (IF) Recommended dilution: 1 : 50- 1 : 5 000 (ICC), 1 : 20- 1 : 2000 (IHC), 1 : 3000 (IF) - Reactivity
-
Confirmed reactivity: Rabbit IgG heavy and light chains (H&L) Predicted reactivity: Rabbit IgG Heavy and Light chains (H&L) - Application Examples
-
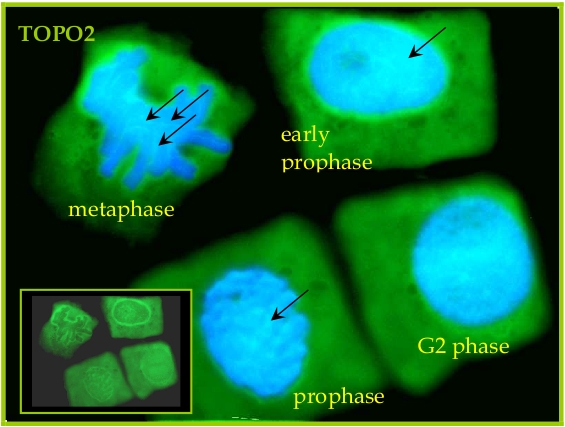
Seeds of field bean (Vicia faba L. subsp. minor var. Nadwiślański; DANKO Group; Sobiejuchy) were sterilized using sodium hypochlorite (0.3% v/v) and germinated in Petri dishes on wetted filter paper at room temperature. At 4 d after imbibition, dark-grown seedlings with primary roots 25±5 mm long were selected for experiments. During incubations roots were oriented horizontally in a humid chamber and aerated continuously on a rotary water-bath shaker (30 rpm) at 23°C. Immunocytochemical assays were performed according to the method prescribed earlier (Rybaczek and Maszewski 2006). Excised apical parts of roots (1.5 mm long) were fixed for 45 min (18°C) in PBS-buffered 3.7% paraformaldehyde, washed several times with PBS and placed in a citric acid-buffered digestion solution (pH 5.0; 37°C for 45 min) containing 2.5% pectinase (Fluka), 2.5% cellulase (Onozuka R-10; Serva) and 2.5% pectoliase (ICN). After removing the digestion solution, root tips were washed 3 times in PBS, rinsed with distilled water and squashed onto Super Frost Plus glass slides (Menzel-Gläser). Air-dried slides were pretreated with PBS-buffered 5% BSA at 20°C for 50 min and incubated overnight in a humidified atmosphere (4°C) with rabbit antibody raised against TOPO2 (Agrisera), dissolved in PBS containing 1% BSA (at a dilution of 1:500). Following incubation, slides were washed 3 times with PBS and incubated for 1 h (18°C) with secondary goat anti-rabbit IgG DyLight®488 antibody (Agrisera, AS09 633, 1:3000). Nuclear DNA was stained with 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenyl-indole (DAPI, 0.4 μg/ml; Sigma-Aldrich). Following washing with PBS, slides were air dried and embedded in Vectashield Mounting Media for Fluorescence (Vector Laboratories). Observations were made using Optiphot-2 fluorescence microscope (Nikon) equipped with B-2A filter (blue light; λ ≈ 495 nm) for DyLight-conjugated antibodies and UV-2A filter (UV light; λ ≈ 365 nm) for DAPI. All images were recorded at exactly the same time of integration using DXM 1200 CCD camera.
Courtesy Dr. Dorota Rybaczek, Lodz University, Poland
Application examples: 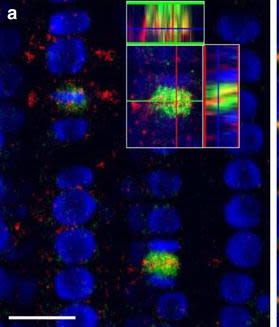
Reactant: Arabidopsis thaliana (Thale cress)
Application: Immunohistochemistry-immunofluorescence
Pudmed ID: 26516341
Journal: Plant Methods
Figure Number: 7A
Published Date: 2015-10-31
First Author: Pasternak, T., Tietz, O., et al.
Impact Factor: 5.139
Open Publication3D reconstruction of Arabidopsis root epidermis cells undergoing telophase: co-localization of ?-Tubulin (TUB) and PIN1 in division plates. Four days old Arabidopsis seedlings were fixed for 30 min in formaldehyde. a Anti-PIN1 mouse monoclonal primary antibody (10A7) diluted 1:50 plus ALEXA Fluor ® 555 anti-mouse as secondary antibody diluted 1:800 (shown in green color) and anti-TUB (AS10 681) rabbit primary antibody diluted 1:600 plus Goat anti-rabbit IgG (H&L), DyLight® 488 Conjugate (AS09 633) diluted in 1:3000 as secondary antibody (shown in red color) were used. b Anti-PIN2 Guinea pig polyclonal primary antibody (clone A193) dilution 1:800 plus ALEXA Fluor ® 555 anti-Guinea pig as the secondary antibody dilution 1:800 (show in green color) and anti-TUB (Agrisera, AS10 681) rabbit primary antibody diluted 1:600 plus Goat anti-rabbit IgG (H&L), DyLight® 488 Conjugate (AS09 633) as secondary antibody diluted in 1:3000 (shown in red color) were used. Co-staining with DAPI visualizes nucleus (blue). Scale bar 20 µm. The Insertion in a shows an ortho-view of dividing cells
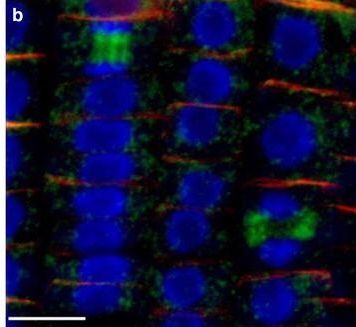
Reactant: Arabidopsis thaliana (Thale cress)
Application: Immunohistochemistry-immunofluorescence
Pudmed ID: 26516341
Journal: Plant Methods
Figure Number: 7b
Published Date: 2015-10-31
First Author: Pasternak, T., Tietz, O., et al.
Impact Factor: 5.139
Open Publication3D reconstruction of Arabidopsis root epidermis cells undergoing telophase: co-localization of ?-Tubulin (TUB) and PIN1 in division plates. Four days old Arabidopsis seedlings were fixed for 30 min in formaldehyde. a Anti-PIN1 mouse monoclonal primary antibody (10A7) diluted 1:50 plus ALEXA Fluor ® 555 anti-mouse as secondary antibody diluted 1:800 (shown in green color) and anti-TUB (AS10 681) rabbit primary antibody diluted 1:600 plus Goat anti-rabbit IgG (H&L), DyLight® 488 Conjugate (AS09 633) diluted in 1:3000 as secondary antibody (shown in red color) were used. b Anti-PIN2 Guinea pig polyclonal primary antibody (clone A193) dilution 1:800 plus ALEXA Fluor ® 555 anti-Guinea pig as the secondary antibody dilution 1:800 (show in green color) and anti-TUB (Agrisera, AS10 681) rabbit primary antibody diluted 1:600 plus Goat anti-rabbit IgG (H&L), DyLight® 488 Conjugate (AS09 633) as secondary antibody diluted in 1:3000 (shown in red color) were used. Co-staining with DAPI visualizes nucleus (blue). Scale bar 20 µm. The Insertion in a shows an ortho-view of dividing cells
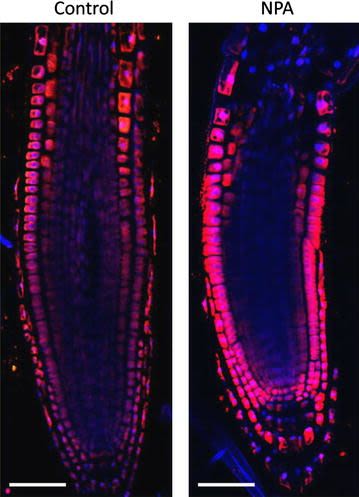
Reactant: Arabidopsis thaliana (Thale cress)
Application: Immunohistochemistry-immunofluorescence
Pudmed ID: 26516341
Journal: Plant Methods
Figure Number: 8A
Published Date: 2015-10-31
First Author: Pasternak, T., Tietz, O., et al.
Impact Factor: 5.139
Open PublicationAuxin immunolocalisation in Arabidopsis roots. Four days old Arabidopsis seedlings were treated with 1 µM 1-N-Naphthylphthalamic acid (NPA) for 24 h to enhance accumulation of auxin in roots. Seedlings were fixed for 20 min in 4 % EDAC in 1× MTSB, and next 30 min in 4 % EDAC+ 2 % Formaldehyde. Anti-indole 3 acetic acid (IAA) rabbit primary antibody (Agrisera, AS06 193) diluted 1:600 plus Goat anti-rabbit IgG (H&L), DyLight® 549 Conjugate (AS09 633) as secondary antibody diluted in 1:3000 (shown in red color) were used. Scale bar 20 µm
- Additional Information
-
Additional information: Concentration: 1.0 mg/ml
Conjugate is present in 10 mM Sodium Phosphate, 0.15 M Sodium Chloride, pH 7.2, 1 % (w/v) BSA, Protease/IgG free. 0.05 % (w/v) sodium azide is added as preservative.DyLight® 488 has a maximum absorbance at 493 nm; Emax = 518 nm.Additional information (application): Based in immunoelectrophoresis, this antibody reacts with heavy chains on rabbit IgG and light chains on all rabbit immunoglobulins.No reactivity is observed to non-immunoglobulin rabbit serum proteins based in immunoelectrophoresis.Purity of this antibody is > 95% based on SDS-PAGE. - Background
-
Background: Goat anti-rabbit IgG, DyLight® 488 Conjugate is a secondary antibody conjugated to DyLight® 488, which binds to all rabbit IgGs in immunological assays.DyLight® is a trademark of Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. and its subsidiaries. - Product Citations
-
Selected references: He et al. (2025). Deciphering the regulatory network underlying auxin depletion-induced fruitlet abscission in litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.). Plant Physiol. 2025 Dec 24:kiaf676. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiaf676.
Huang et al. (2025). PagKNAT5a Promotes Plant Growth by Enhancing Xylem Cell Elongation and Secondary Wall Formation in Poplar. Hortic Res. 2025 May 7;12(8):uhaf125. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhaf125.
Burchardt et al. (2024). Exploring the response of yellow lupine (Lupinus luteus L.) root to drought mediated by pathways related to phytohormones, lipid, and redox homeostasis. BMC Plant Biol . 2024 Nov 6;24(1):1049. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05748-4.
Kamińska et al. (2024). Comprehensive elucidation of the differential physiological kale response to cytokinins under in vitro conditions. BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Jul 15;24(1):674.doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05396-8.
Zhao, Deng, Qian, et al. (2022) Arabidopsis ABCG14 forms a homodimeric transporter for multiple cytokinins and mediates long-distance transport of isopentenyladenine-type cytokinins [published online ahead of print, 2022 Oct 28]. Plant Commun. 2022;100468. doi:10.1016/j.xplc.2022.100468
Kucko et al. (2022) The acceleration of yellow lupine flower abscission by jasmonates is accompanied by lipid-related events in abscission zone cells, Plant Science, Volume 316, 2022,111173, ISSN 0168-9452, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2021.111173.
Namyslov et al. (2020). Exodermis and Endodermis Respond to Nutrient Deficiency in Nutrient-Specific and Localized Manner. Plants (Basel). 2020 Feb 6;9(2). pii: E201. doi: 10.3390/plants9020201. (immunolocalization)
Fizesan et al. (2018). Responsiveness assessment of a 3D tetra-culture alveolar model exposed to diesel exhaust particulate matter. Toxicol In Vitro. 2018 Aug 3;53:67-79. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2018.07.019.
Liu et al. (2016). Fold formation at the compartment boundary of Drosophila wing requires Yki signaling to suppress JNK dependent apoptosis. Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 29;6:38003. doi: 10.1038/srep38003.
Wang et al. (2016). Complementary expression of optomotor-blind and the Iroquois complex promotes fold formation to separate wing notum and hinge territories. Dev Biol. 2016 Aug 1;416(1):225-34. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.05.020. Epub 2016 May 19
Kaulmann et al. (2016). Inflammation related responses of intestinal cells to plum and cabbage digesta with differential carotenoid and polyphenol profiles following simulated gastro-intestinal digestion. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2016 Mar 18. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201500947.
Jimenez-Lopez et al. (2015). Biogenesis of protein bodies during legumin accumulation in developing olive (Olea europaea L.) seed. Protoplasma. 2015 May 21. - Reviews:
-
Zienkiewicz A | 2018-11-15The antibody works great for both Western Blotting and immunolocalization! There is practically no background. Ever since we use this antibody.