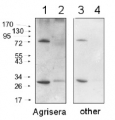
1

Anti-XTH-Xet | XET5 Xyloglucan xyloglucosyl transferase
AS08 319 | Clonality: Polyclonal | Host: Rabbit | Reactivity: Hordeum vulgare, Oryza sativa
- Product Info
-
Immunogen: Two synthetic peptides from highly conserved region of Horderum vulgare XTH-Xet
Host: Rabbit Clonality: Polyclonal Purity: Serum Format: Lyophilized Quantity: 100 µl Reconstitution: For reconstitution add 100 µl of sterile water Storage: Store lyophilized/reconstituted at -20°C; once reconstituted make aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Please remember to spin the tubes briefly prior to opening them to avoid any losses that might occur from material adhering to the cap or sides of the tube. Tested applications: ELISA (ELISA), Western blot (WB) Recommended dilution: 1 : 5000 (ELISA), 1 : 500 (WB) Expected | apparent MW: 31.5 | 33 kDa - Reactivity
-
Confirmed reactivity: Hordeum vulgare, Oryza sativa
Predicted reactivity: Species of your interest not listed? Contact us Not reactive in: Poplar sp., Zea mays
- Background
-
Background: Molecular interactions between wall polysaccharides, which include cellulose and a range of non-cellulosic polysaccharides such as xyloglucans and (1,3;1,4)-?-d-glucans, are fundamental to cell wall properties. These interactions have been assumed to be non-covalent in nature in most cases. A highly purified barley xyloglucan xyloglucosyl transferase HvXET5 (EC 2.4.1.207), a member of the GH16 group of glycoside hydrolases, catalyses the in vitro formation of covalent linkages between xyloglucans and cellulosic substrates, and between xyloglucans and (1,3;1,4)-?-d-glucans. It is possible that XETs could link different polysaccharides in vivo, and hence influence cell wall strength, flexibility and porosity.
- Product Citations
-
Selected references: Soyama et al. (2025). Irregular Swelling of Tomato Fruit Chambers During the Early Stages of Fruit Formation is Due to the Local Distribution of Cell Wall-Loosening Proteins Under Ca-deficient Conditions. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation.
Tsuchiya et al. (2015). Distribution of XTH, expansin, and secondary-wall-related CesA in floral and fruit abscission zones during fruit development in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Front Plant Sci. 2015 May 15;6:323. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00323.
Liu et al. (2013). Brittle Culm1, a COBRA-Like Protein, Functions in Cellulose Assembly through Binding Cellulose Microfibrils. PLoS Genet 9(8): e1003704. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1003704 (Oryza sativa, western blot)
Hrmova et al. (2007) A barley xyloglucan xyloglucosyl transferase covalently links xyloglucan, cellulosic substrates and (1,3;1,4)-β. J. Biol. Chem. 82: 12951-12962. - Reviews:
-
Anna | 2018-05-21Western blotting application: cell walls were isolated from Arabidopsis thaliana tissue, proteins were extracted and concentrated, 20ug of protein extracts were separated in SDS 12% acrilamide gel. Primary antibodies were used at 1/500 dilution, standard immunoblotting procedure was applied using nitrocellulose membranes. Protein visualisation gives satisfactory results, published in Podgorska et al. 2017, Front. Plant Sci. 8:1344