1
Anti-5MeC | 5-Methylcytosine (clone 5MC-CD)
AS21 4559 | Clonality: Monoclonal | Host: Mouse | Reactivity: 5-Methylcytosine
- Product Info
-
Immunogen: BSA-conjugated 5-Methylcytosine Sub class: IgM Host: Mouse Clonality: Monoclonal Purity: Purified IgM in PBS. Contains 50 % glycerol, filter sterilized. Format: Liquid Quantity: 100 µg Storage: Store at -20°C; make aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Please remember to spin the tubes briefly prior to opening them to avoid any losses that might occur from material adhering to the cap or sides of the tube. Tested applications: Immunofluorescence (IF), Western blot (WB) Recommended dilution: 1:50 - 1: 100 (IF), 1 : 1000 (WB) - Reactivity
-
Confirmed reactivity: Chlamydmonas me-1 cells, mouse embryonic stem cells Predicted reactivity: DNA with 5-Methylcytosine (methylated DNA) - Application Examples
-
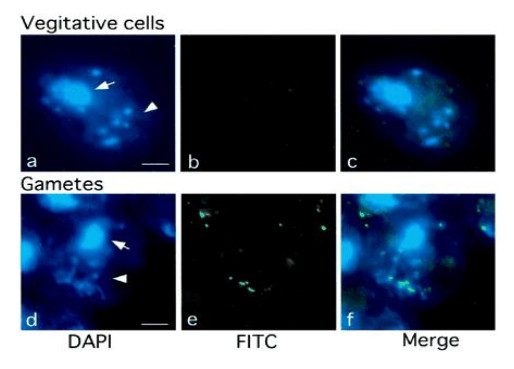
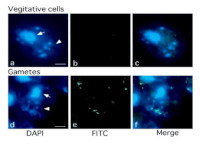
Methylation of chloroplast DNA of Chlamydomonas me-1 cells, visualized by anti-5-methylcytosine antibodies.
Left: DAPI stained cells. Middle: Cells stained with anti-5MeC antibodies, followed by secondary anti-mouse IgM, FITC conjugated secondary antibodies, Right: Merged image.
Chloroplast DNA is exclusively methylated in gamete cells. Described in Nishiyama et al. 2002.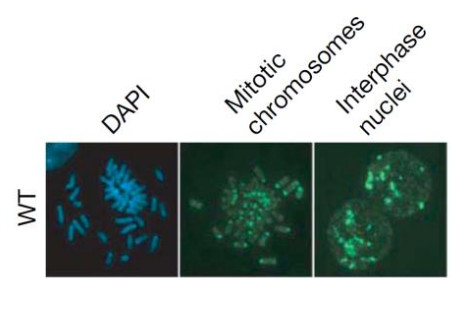
Intense 5-methylcytosine staining at pericentromeric regions of mouse embryonic stem cells was seen in the mitotic chromosome and interphase nuclei of ESCs. Described in Sharif et al. 2007.
- Background
-
Background: DNA methylation is a type of chemical modification of DNA that can be inherited and subsequently removed without changing the original DNA sequence. Therefore it is part of the epigenetic code and is also the most well characterized epigenetic mechanism. DNA methylation results in addition of a methyl group to DNA — for example, to the number 5 carbon of the cytosine pyrimidine ring — which involves reduction in gene expression. In adult somatic tissues, DNA methylation typically occurs in a CpG dinucleotide context; non-CpG methylation is prevalent in embryonic stem cells. - Product Citations
-
Selected references: Sharif et al. (2007) The SRA protein Np95 mediates epigenetic inheritance by recruiting Dnmt1 to methylated DNA. Nature. 2007 Dec 6;450(7171):908-12. doi: 10.1038/nature06397. Epub 2007 Nov 11. PMID: 17994007.
Nishiyama et al. (2002) A chloroplast-resident DNA methyltransferase is responsible for hypermethylation of chloroplast genes in Chlamydomonas maternal gametes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Apr 30;99(9):5925-30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.082120199. PMID: 11983892; PMCID: PMC122878.
Sano, Imokawa & Sager (1988) Detection of heavy methylation in human repetitive DNA subsets by a monoclonal antibody against 5-methylcytosine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Nov 10;951(1):157-65. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90036-x. PMID: 2847796.
Sano, Royer & Sager (1980) Identification of 5-methylcytosine in DNA fragments immobilized on nitrocellulose paper. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3581-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3581. PMID: 6251470; PMCID: PMC349661.
- Protocols
-
Agrisera Western Blot protocol and video tutorials
- Reviews:
-
This product doesn't have any reviews.