1
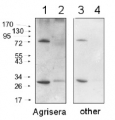
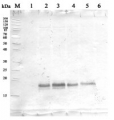
Anti-ADK | Adenylate kinase
AS16 3155 | Clonality: Polyclonal | Host: Rabbit | Reactivity: E. coli
- Product Info
-
Immunogen: Protein derived from Escherichia coli, Uniprot: P69441
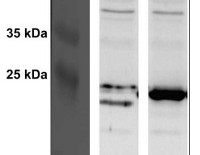
Host: Rabbit Clonality: Polyclonal Purity: Serum Format: Lyophilized Quantity: 50 µl Reconstitution: For reconstitution add 50 µl, of sterile water Storage: Store lyophilized/reconstituted at -20°C; once reconstituted make aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Please remember to spin the tubes briefly prior to opening them to avoid any losses that might occur from material adhering to the cap or sides of the tube. Tested applications: Western blot (WB) Recommended dilution: 1: 100 000 (WB) Expected | apparent MW: 23.5 kDa (E.coli), 24.3 kDa (S.cerevisiae)
- Reactivity
-
Confirmed reactivity: Escherichia coli Predicted reactivity: Not reactive in: No confirmed exceptions from predicted reactivity are currently known - Application Examples
-
Application example 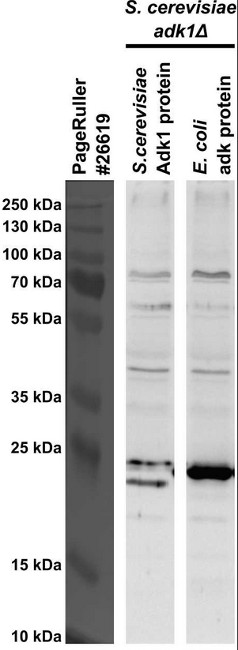
Protein samples were prepared using TCA-extraction method. S. cerevisiae adk1Δ strains expressing either S. cerevisiae Adk1 protein (24.3 kDa) or E. coli adk protein (23.5 kDa) were cultivated logarithmically, and 5 OD-units of cells were collected for TCA-extraction method. In the end, protein pellets were re-suspended with 300 μl of TCA-Laemmli Loading Buffer and denatured at 100°C for 10 minutes. Total protein samples (8 μl of each sample) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes using a wet transfer protocol. The membranes were blocked with 5% dry-milk in 1x TBST for 1.5 hours at room temperature (RT) with agitation and then they were incubated with primary antibody (anti-adk antibody, 1:2,000) in 5% dry-milk in 1x TBST overnight at 4°C with agitation. The primary antibody solution was decanted and the membranes were washed 3 times for 10 minutes with 1x TBST with agitation. The membranes were then incubated with secondary antibody (HRP conjugated anti-rabbit IgG, 1:4,000) in 5% dry-milk in 1x TBST for 1 hour at RT with agitation. The membranes were washed as above and the signals were detected using chemiluminescent detection reagent and exposing the membranes in LAS4000 machine (GE-healthcare) for 10 seconds. Followed-up experiments revealed that lowering the primary antibody concentration from 1:2,000 to 1:50,000-100,000 reduces the unspecific background signals and lowers the risk of target signal oversaturation.
Courtesy of Dr. Hasan Tukenmez, Umeå University, Sweden - Background
-
Background: Adenylate kinase (ADK) is important in cellular energy homeostasis. It is a phosphotransferase enzyme, catalyzing the interconversion of adenine nucleotides.
Alternative name: myokinase - Product Citations
-
Selected references: Tükenmez et al. (2016). Linkage between Fitness of Yeast Cells and Adenylate Kinase Catalysis. PLoS One. 2016 Sep 19;11(9):e0163115. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163115. eCollection 2016. - Protocols
-
- Reviews:
-
This product doesn't have any reviews.