1
Anti-AtpC | Gamma subunit of ATP synthase (chloroplastic)
AS08 312 | Clonality: Polyclonal | Host: Rabbit | Reactivity: Arabidopsis thaliana, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, Chlorella sorokiniana, Chlorella vulgaris, Echinochloa crus-galli, Pisum sativum, Physcomitrella patens, Zea mays
- Product Info
-
Immunogen: KLH-conjugated peptide, derived from C-terminal part of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii protein sequence A8HXL8 Host: Rabbit Clonality: Polyclonal Purity: Serum Format: Lyophilized Quantity: 100 µl Reconstitution: For reconstitution add 100 µl of sterile water Storage: Store lyophilized/reconstituted at -20°C; once reconstituted make aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Please remember to spin the tubes briefly prior to opening them to avoid any losses that might occur from material adhering to the cap or sides of the tube. Tested applications: Western blot (WB) Recommended dilution: 1: 1000 (ELISA), 1: 10 000 (WB)
Expected | apparent MW: 35.3 | 42 (Chlamydomonas reinhardtii)
35.6 | 38 (Spinacia oleracea)
- Reactivity
-
Confirmed reactivity: Arabidopsis thaliana, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, Chlorella sorokiniana, Chlorella vulgaris, Echinochloa crus-galli, Phycomitrella patens, Pisum sativum, Zea mays
Predicted reactivity: Arachis hypogaea, Auxenochlorella protothecoides, Bathycoccus prasinos, Cephalotus follicularis, Cicer arietinum, Coccomyxa subellipsoidea (strain C-169), Cucumis melo, Cyanobacteria, Cynara cardunculus var. scolymus, Daucus carota subsp. sativus, Dendrobium catenatum,Fagus sylvaticaGenlisea aurea, Glycine max, Gossypium hirsutum, Jatropha curcas, Juglans regia, Klebsormidium flaccidum, Helianthus annuus, Lactuca sativa, Lens culinaris, Lupinus angustifolius, Manichot esculenta, Marchantia polymorpha subsp. ruderalis, Medicago truncatula, Micromonas pusilla (strain CCMP1545), Monoraphidium neglectum, Morus notabilis, Nelumbo nucifera, Nicotiana sylvestris, Nicotiana tabacum,Oryza sativa, Ostreococcus tauri, Punica granatum , Phaseolus vulgaris, Pisum sativum, Populus jackii, Populus trichocarpa, Prunus persica, Ricinus communis, Rosa chinensis, Selaginella moellendorffii, Spinacia oleracea,Solanum lycopersicum, Solanum tuberosum, Terma orientalis, Tetraselmis sp. GSL018, Theobroma cacao, Trifolium pratense, Zostera marina, Vigna unguiculata, Vitis vinifera, Volvox carteri f. nagariensis, Quercus suber
Species of your interest not listed? Contact usNot reactive in: Phaeodactylum tricornutum - Application Examples
-
Application example
.jpg)
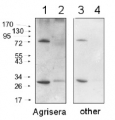
10 ug of chlorophyll/well of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii total cell extract (1), Chlamydomonas reinhardtii subunit gamma deletion mutant thylakoid membrane fraction (2), Arabidospsis thaliana thylakoid membrane fraction (3), Chlamydomonas reinhardtii thylakoid membrane preparation (4) were separated on 12-18% acrylamide-8M urea gel and blotted to nitrocellulose membrane. Filters were blocked 1 h with 5% dry milk in 1 x PBS and probed with anti-ATP synthase subunit gamma antibody (AS08 312, 1: 25 000, 1h) and secondary HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit antibody (1: 10 000, 1 h) in 1 x PBS containing 5% dry milk. All steps were performed at RT with agitation. Signal was detected with chemiluminescent detection reagent, exposure time 30’’ and 3 min (overexposed).
Arabidopsis membrane preparation has been done according to Lezhneva et al. (2008) A novel pathway of cytochrome c biogenesis is involved in the assembly of the cytochrome b6f complex in arabidopsis chloroplasts. J Biol. Chem., 283:24608-24616 and Chlamydomonas membranes were prepared according to Chua & Bennoun (1975) Thylakoid membrane polypeptides of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: wild-type and mutant strains deficient in photosystem II reaction center. PNAS 72:2175-2179
Courtesy Dr. Yves Choquet, French National Centre for Scientific Research, France
Application examples: 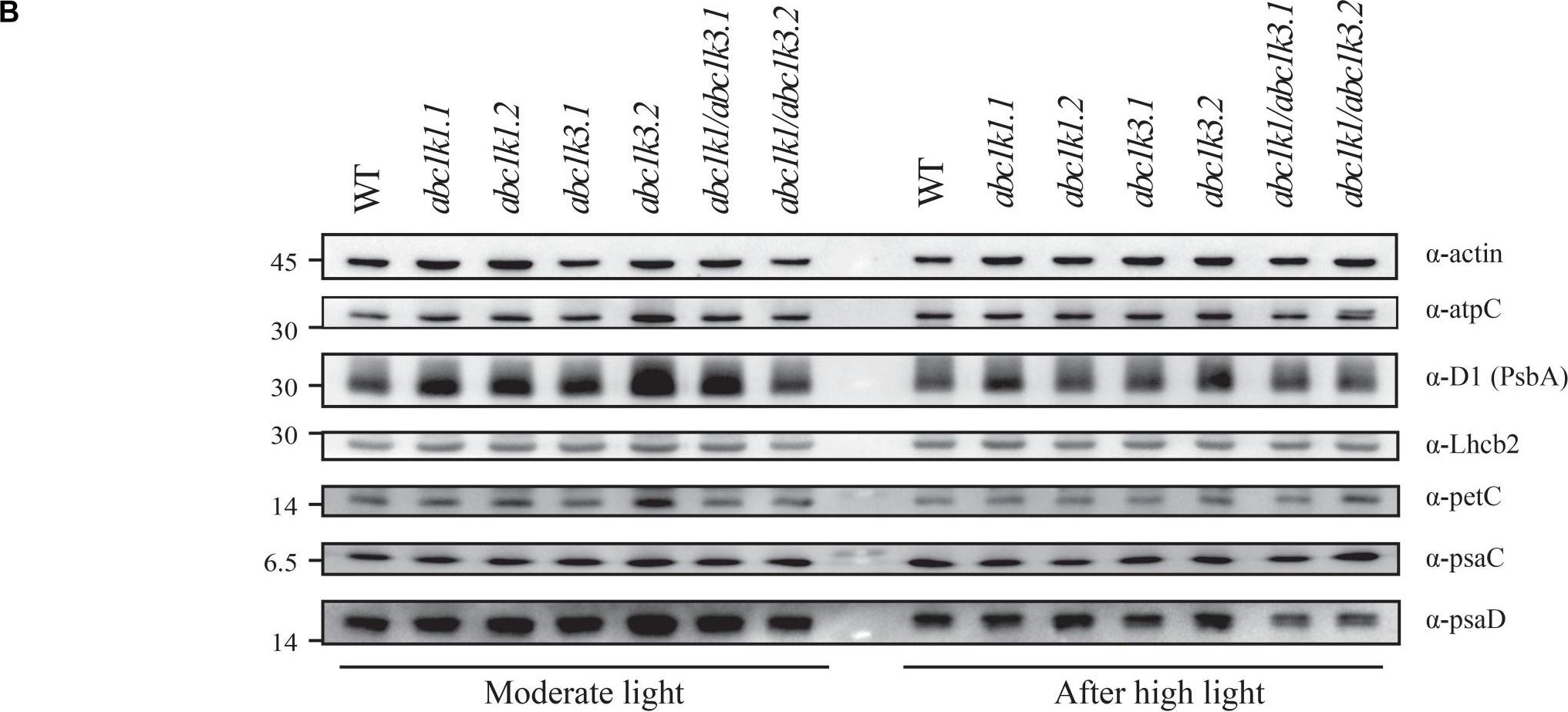
Reactant: Arabidopsis thaliana (Thale cress)
Application: Western Blotting
Pudmed ID: 32269582
Journal: Front Plant Sci
Figure Number: 7B
Published Date: 2020-04-10
First Author: Pralon, T., Collombat, J., et al.
Impact Factor: 5.435
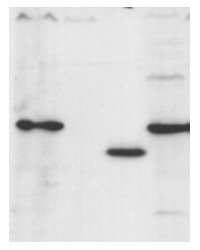
Open PublicationDouble mutant maintains thylakoid protein phosphorylation and state transitions after high light. (A) Total protein extracts of wild type (WT), abc1k1.1, -2, abc1k3.1, -2, and abc1k1/abc1k3.1, -2 light-exposed leaves were separated by SDS PAGE, transferred on nitrocellulose membrane and decorated with anti-phosphothreonine antibody. The main thylakoid phospho-proteins are indicated on the right according to their size. Core photosystem II proteins D1 (PsbA) and D2 (PsbD) are indicated together due their poor resolution. (B) The accumulation of the principal photosynthetic complexes was assessed using antibodies against specific subunits of each complex: anti-Lhcb2 for the major LHCII, anti-D1 (PsbA) for PSII, anti-PetC for cytochrome b6f, anti-PsaD and anti-PsaC for PSI, and anti-AtpC for ATP synthase. Actin signal is shown as a loading control. (C) Fluorescence quenching related to the state transitions (qT) of wild type (WT), abc1k1.1, -2, abc1k3.1, -2, and abc1k1/abc1k3.1, -2 under moderate light (120 ?mol of photons m–2 s–1) (ML) and after 3 h of high light (500 ?mol of photons m–2 s–1) (HL). qT was calculated from the maximal chlorophyll fluorescence measured after 10 min exposure to red light (660 nm) supplemented with far-red illumination (720 nm) “State 1” (FMST1) or to pure red light “State 2” (FMST2). Quenching related to state transition was calculated as qT = (FMST1 – FMST2)/FM. Each value represents the average of a pot containing 2–3 plants. Superscript letters are used to indicate statistically different groups (p < 0.05) by paired Student’s t-test.
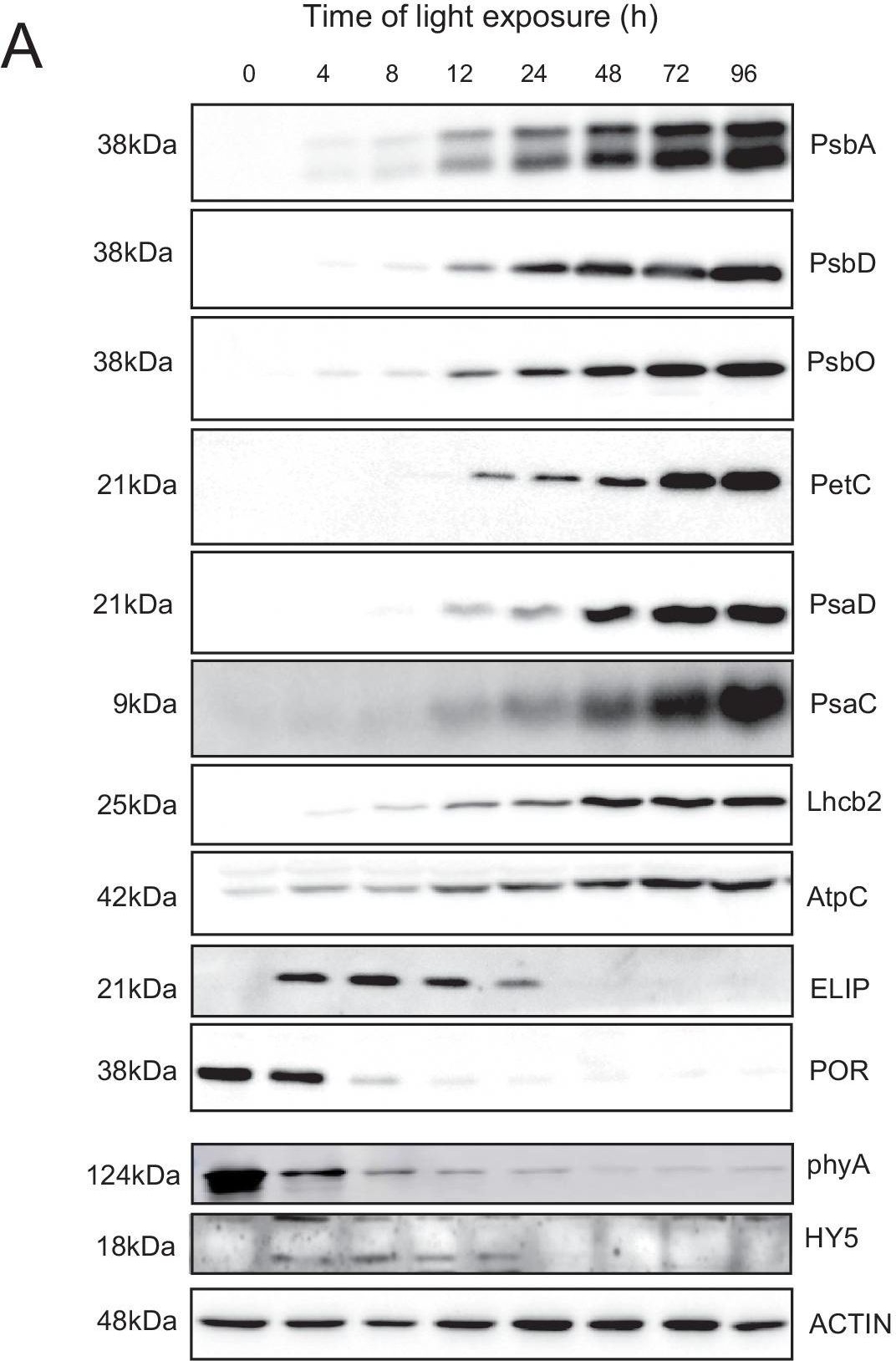
Reactant: Arabidopsis thaliana (Thale cress)
Application: Western Blotting
Pudmed ID: 33629953
Journal: Elife
Figure Number: 6A
Published Date: 2021-02-25
First Author: Pipitone, R., Eicke, S., et al.
Impact Factor: 7.448
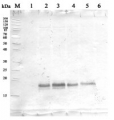
Open PublicationAccumulation dynamics of photosynthesis-related proteins during de-etiolation.Three-day-old etiolated seedlings of Arabidopsis thaliana were illuminated for 0 hr (T0), 4 hr (T4), 8 hr (T8), 12 hr (T12), 24 hr (T24), 48 hr (T48), 72 hr (T72), and 96 hr (T96) under white light (40 µmol/m2/s). (A) Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred onto nitrocellulose membrane and immunodetected with antibodies against PsbA, PsbD, PsbO, PetC, PsaD, PsaC, Lhcb2, AtpC, ELIP, POR, phyA, HY5, and ACTIN proteins. (B–C) Quantification of PsbA, PetC, and PsaC during de-etiolation. Heatmap (B) was generated after normalization of the amount of each protein relative to the last time point (T96). Graph (C) corresponds to the absolute quantification of proteins at T96. Error bars indicate ± SD (n = 3). Quantification of photosystem-related proteins during de-etiolation is detailed in Figure 6—figure supplement 1.Figure 6—source data 1.Quantitative data for immunoblot analysis.Quantitative data for immunoblot analysis.Quantification of photosynthesis-related proteins.(A) Immunodetection of PsbA, PetC, and PsaC during de-etiolation. Dilutions were used for the later time points to avoid saturation of the signal. (B) Different bands were detected by Amersham Imager program and quantified by Image QuantTL (Amersham). (C) Calibration curves were created using recombinant proteins (Agrisera). Calibration curve composition: PsbA 10 ng (A; lane a), 5 ng (b), 2.5 ng (c), and 1.25 ng (d); PetC 10 ng (e), 5 ng (f), 2.5 ng (g), and 1.25 ng (h); PsaC 3 ng (i), 1.5 ng (l), 0.75 ng (m), and 0.325 ng (n). Data indicate mean ± SD (n = 3–4). Raw data and calculations are shown in Figure 6—source data 1.
- Additional Information
-
Additional information: This product can be sold containing ProClin if requested Additional information (application): Apparent molecular weight of subunit gamma (and as general rule most of ATP synthase subunits) is quite different between Chlamydomonas (42 kDa) and higher plants (38 kDa in spinach), see figure in Lemaire et al. (1989).
- Background
-
Background: ATP synthase produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane. F-type ATPases have two components, CF(1) - the catalytic core - and CF(0) - the membrane proton channel. CF(1) has five subunits: alpha(3), beta(3), gamma(1), delta(1), epsilon(1). CF(0) has three main subunits: a, b and c. The gamma chain is believed to be important in regulating ATPase activity and the flow of protons through the CF(0) complex. Alternative name of gamma subunit is also: F-ATPase gamma subunit.
- Product Citations
-
Selected references: Kafri et al. (2023). Systematic identification and characterization of genes in the regulation and biogenesis of photosynthetic machinery. Cell. 2023 Dec 7;186(25):5638-5655.e25.doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.11.007.
Pipitone et al. (2021). A multifaceted analysis reveals two distinct phases of chloroplast biogenesis during de-etiolation in Arabidopsis. Elife. 2021 Feb 25;10:e62709. doi: 10.7554/eLife.62709. PMID: 33629953; PMCID: PMC7906606.
Storti et al. (2020). The activity of chloroplast NADH dehydrogenase-like complex influences the photosynthetic activity of the moss Physcomitrella patens. doi.org/10.1101/2020.01.29.924597
Pralon et al. (2019). Plastoquinone homoeostasis by Arabidopsis proton gradient regulation 6 is essential for photosynthetic efficiency. Commun Biol. 2019 Jun 20;2:220. doi: 10.1038/s42003-019-0477-4.
Li et al. (2019). A genome-wide algal mutant library and functional screen identifies genes required for eukaryotic photosynthesis. Nat Genet. 2019 Apr;51(4):627-635. doi: 10.1038/s41588-019-0370-6.
Liang et al. (2018). Thylakoid-Bound Polysomes and a Dynamin-Related Protein, FZL, Mediate Critical Stages of the Linear Chloroplast Biogenesis Program in Greening Arabidopsis Cotyledons. Plant Cell. 2018 Jul;30(7):1476-1495. doi: 10.1105/tpc.17.00972. Epub 2018 Jun 7.
Storti et al. (2018). Role of cyclic and pseudo-cyclic electron transport in response to dynamic light changes in Physcomitrella patens. Plant Cell Environ. 2018 Nov 29. doi: 10.1111/pce.13493.
Schmid et al. (2018). PUMPKIN, the sole Plastid UMP Kinase, Associates with Group II Introns and Alters Their Metabolism. Plant Physiol. 2018 Nov 8. pii: pp.00687.2018. doi: 10.1104/pp.18.00687.
Nikkanen et al. (2018). Regulation of chloroplast NADH dehydrogenase-like complex by NADPH-dependent thioredoxin system. CSH, BioRixiv. doi.org/10.1101/261560.
Nikkanen et al. (2016). Crosstalk between chloroplast thioredoxin systems in regulation of photosynthesis. Plant Cell Environ. 2016 Aug;39(8):1691-705. doi: 10.1111/pce.12718.
Naranjo et al. (2015). The chloroplast NADPH thioredoxin reductase C, NTRC, controls non-photochemical quenching of light energy and photosynthetic electron transport in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2015 Oct 17. doi: 10.1111/pce.12652.
Dwyer et al. (2012). Antisense reductions in the PsbO protein of photosystem II leads to decreased quantum yield but similar maximal photosynthetic rates. J. Ex. Bot. 63(13):4781-95. - Protocols
-
Agrisera Western Blot protocol and video tutorials
Protocols to work with plant and algal protein extracts
Oxygenic photosynthesis poster by prof. Govindjee and Dr. Shevela
Z-scheme of photosynthetic electron transport by prof. Govindjee and Dr. Björn and Dr. Shevela - Reviews:
-
Ruby C | 2015-04-14Ab was used at a specified concentration (1:10,000) on a 12% SDS-PAGE for western blot detection. Very reliable but occasionally resulted in additional non-specific bands. Highly recommend.MIO CRUZ | 2015-02-20We use Arabidopsis thaliana whole leaf as sample. 1:10000(WB) works great!