Anti-ExoS | Exoenzyme S
AS05 056 | Clonality: polyclonal | Host: Hen | Reactivity: Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Product Info
-
Immunogen: amino acids 366 to 453 of PA3841 of ADP-rbosylating enzyme - Exoenzyme S overexpressed in a GST fusion. Afterwards cleaved with a help of trombin and separated on a polyacrylamide gel. Gel piece has been used for immunizations.
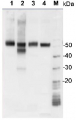
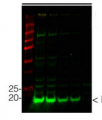
Host: Chicken Clonality: Polyclonal Purity: Purified, total IgY (chicken egg yolk immunoglobulin) in PBS pH 8. Contains 0.02 % sodium azide. Format: Liquid Quantity: 100 µl Storage: Store at 4°C; make aliquots to avoid working with a stock. Please remember to spin the tubes briefly prior to opening them to avoid any losses that might occur from material adhering to the cap or sides of the tube. Tested applications: Western blot (WB) Recommended dilution: 1 : 5000 (WB) Expected | apparent MW: 48 kDa
- Reactivity
-
Confirmed reactivity: Pseudomonas aeruginosa Predicted reactivity: Pseudomonas aeruginosa Not reactive in: No confirmed exceptions from predicted reactivity are currently known - Background
-
Background: Exoenzyme S (ExoS) is a toxin directly translocated into eukaryotic cells by the type III secretory process of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. It is a bi-functional toxin and contain an N-terminal Rho GAP domain that disrupts the actin cytoskeleton and interference of phagocytosis. The C-terminal of ExoS contains an ADP-ribosyltransferase domain, which elicits a cytotoxic phenotype in cultured cells.
- Product Citations
-
Selected references: Feng et al. (2019: Tanshinones: First-in-Class Inhibitors of the Biogenesis of the Type 3 Secretion System Needle of Pseudomonas aeruginosa for Antibiotic Therapy. ACS Cent. Sci.2019.
Anantharajah et al. (2017). Salicylidene acylhydrazides and hydroxyquinolines act as inhibitors of type three secretion systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by distinct mechanisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Apr 10. pii: AAC.02566-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02566-16.
Anantharajah et al. (2016). Inhibition of the Injectisome and Flagellar Type III Secretion Systems by INP1855 Impairs Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pathogenicity and Inflammasome Activation. J Infect Dis. 2016 Jul 13. pii: jiw295.
- Protocols
- Western blot using IgY antibodies
- Reviews:
-
This product doesn't have any reviews.