1
DISCONTINUED Anti-PsaK | PSI-K subunit of photosystem I
AS04 049 | Clonality: Polyclonal | Host: Rabbit | Reactivity: A. thaliana, H. vulgare, N. tabacum, S. oleracea
Replaced by AS23 4919
- Product Info
-
Immunogen: Fusion protein between DHFR and the mature part of PsaK from Arabidopsis thaliana, UniProt: Q9SUI5, TAIR: At1g30380
Host: Rabbit Clonality: Polyclonal Purity: Total IgG. Protein G purified in PBS pH 7.4. Format: Lyophilized Quantity: 100 µl Reconstitution: For reconstitution add 100 µl of sterile water Storage: Store lyophilized/reconstituted at -20°C; once reconstituted make aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Please remember to spin the tubes briefly prior to opening them to avoid any losses that might occur from material adhering to the cap or sides of the tube. Tested applications: Western blot (WB) Recommended dilution: 1 : 2000-1 : 5000 (WB) Expected | apparent MW: 8.5 kDa - Reactivity
-
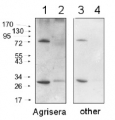
Confirmed reactivity: Arabidopsis thaliana, Hordeum vulgare, Nicotiana tabacum, Spinacia oleracea Predicted reactivity: Zea mays
Species of your interest not listed? Contact usNot reactive in: Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, Cyanidioschyzon merolae strain 10D, Synechococcus sp. PCC 7942
- Application Examples
-
Application example
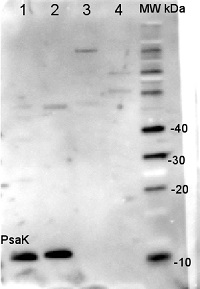
2 µg of total protein from Arabidopsis thaliana leaf (1), Horderum vulgare leaf (2), Chlamydomonas reinhardtii total cell (3), Synechococcus sp. PCC 7942 total cell (4), all extracted with PEB (AS08 300) and separated on 4-12% NuPage (Invitrogen) LDS-PAGE and blotted 1h to PVDF. Blots were blocked immediately following transfer in 2% blocking reagent in 20 mM Tris, 137 mM sodium chloride pH 7.6 with 0.1% (v/v) Tween-20 (TBS-T) for 1h at room temperature with agitation. Blots were incubated in the primary antibody at a dilution of 1: 10 000 for 1h at room temperature with agitation. The antibody solution was decanted and the blot was rinsed briefly twice, then washed once for 15 min and 3 times for 5 min in TBS-T at room temperature with agitation. Blots were incubated in secondary antibody (anti-rabbit IgG horse radish peroxidase conjugated) diluted to 1:20 000 in 2% blocking solution for 1h at room temperature with agitation. The blots were washed as above and developed for 5 min with chemiluminescent detection reagent according the manufacturers instructions. Images of the blots were obtained using a CCD imager (FluorSMax, Bio-Rad) and Quantity One software (Bio-Rad).
Application examples: 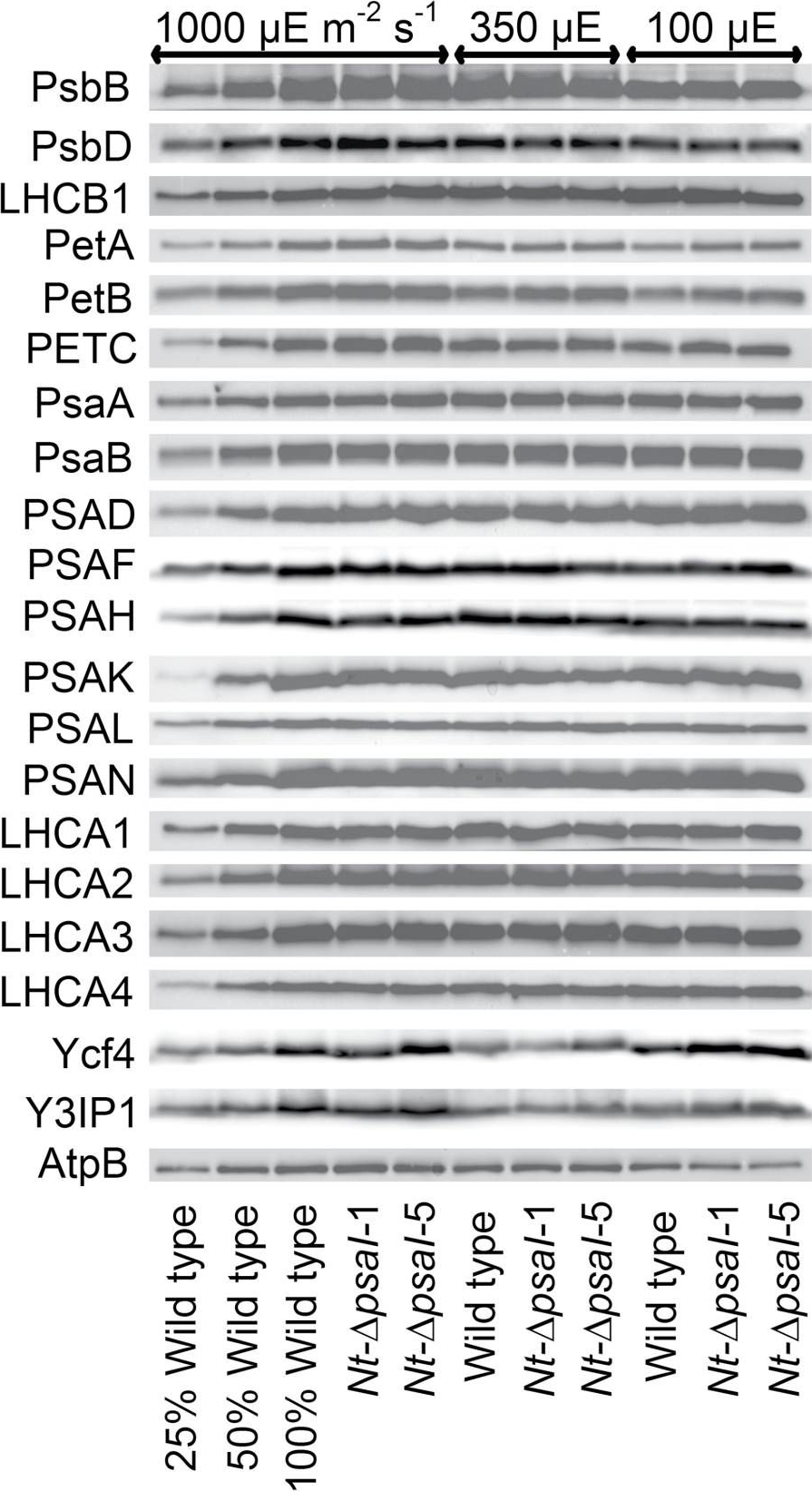
Reactant: Nicotiana tabacum (Common tobacco)
Application: Western Blotting
Pudmed ID: 28180288
Journal: J Exp Bot
Figure Number: 5A
Published Date: 2017-02-01
First Author: Schöttler, M. A., Thiele, W., et al.
Impact Factor: 6.088
Open PublicationImmunoblot analysis of photosynthetic complex accumulation in wild-type tobacco and the two ?psaI lines grown under low, intermediate, and high-light conditions. Because the accumulation of most tested proteins was highest under high-light conditions, lanes one to three contain samples diluted to 25%, 50%, and a 100% sample of wild-type tobacco grown under high-light conditions, to allow for semi-quantitative determination of changes in protein abundance. Lanes four and five contain the two transplastomic lines grown at 1000 µE m?2 s?1. Lanes six to eight contain wild-type tobacco and the mutants grown at intermediate light intensities, and lanes nine to eleven contain samples grown at low light intensities. For PSII, the accumulation of the essential subunits PsbB (CP43) and PsbD (D2) and the LHCB1 antenna protein were determined, while for the cytochrome b6f complex, the accumulation of the essential redox-active subunits PetA (cytochrome f), PetB (cytochrome b6), and PETC (Rieske FeS protein) was tested. AtpB was probed as an essential subunit of the chloroplast ATP. For PSI, in addition to the three essential plastome-encoded subunits PsaA, PsaB, and PsaC, the accumulation of the nuclear-encoded subunits PSAD, PSAH, PSAK, PSAL, and PSAN and of the four LHCI proteins (LHCA1, LHCA2, LHCA3, LHCA4) was determined. Finally, we examined the accumulation of Ycf4, the chloroplast-encoded PSI-biogenesis factor encoded in the same operon as PsaI, and the nuclear-encoded assembly factor Y3IP1.
- Background
-
Background: PsaK is a subunit of photosystem I. It has a role in organizing the peripheral light-harvesting complexes on the core antenna of photosystem I. Alternative names: photosystem I subunit X, PSI-K
- Product Citations
-
Selected references: Bock (2012). The plastid genome-encodedYcf4 protein functions as a non-essential assembly factor for photosystem I in higher plants. Plant Physiol. ahead of print. - Protocols
-
Agrisera Western Blot protocol and video tutorials
Protocols to work with plant and algal protein extracts - Reviews:
-
This product doesn't have any reviews.