1

Anti-TYLCV V2 | Tomato yellow leaf curl virus coat protein V2
AS15 3059 | Clonality: Polyclonal | Host: Rabbit | Reactivity: Tomato yellow leaf curl virus coat protein V2
LIMITED STOCK
- Product Info
-
Immunogen: Recombinant fragment of V2 protein as described in Gorovits et al. (2013). Host: Rabbit Clonality: Polyclonal Purity: Serum Format: Lyophilized Quantity: 150 �l Reconstitution: For reconstitution add 150 �l of sterile water Storage: Store lyophilized/reconstituted at -20�C; once reconstituted make aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Please remember to spin the tubes briefly prior to opening them to avoid any losses that might occur from material adhering to the cap or sides of the tube. Tested applications: Immunolocalization (IL), Western blot (WB) Recommended dilution: 1 : 500-1 : 1000 (IL), 1 : 200 (WB) Expected | apparent MW: 13 kDa
- Reactivity
-
Confirmed reactivity: Tomato yellow leaf curl virus coat 13 kDa Predicted reactivity: Tomato yellow leaf curl virus coat 13 kDa Not reactive in: No confirmed exceptions from predicted reactivity are currently known - Application Examples
-
Application examples: 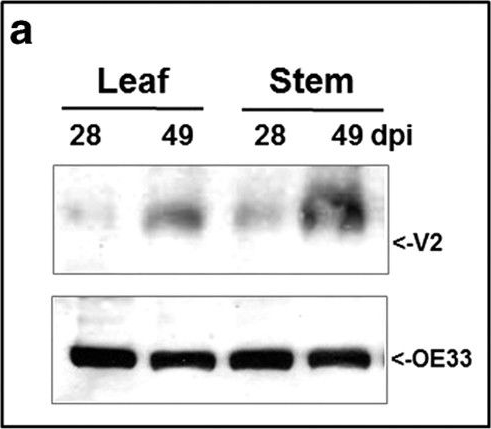
Reactant: Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato)
Application: Western Blotting
Pudmed ID: 25940862
Journal: Sci Rep
Figure Number: 1A
Published Date: 2015-05-05
First Author: Moshe, A., Belausov, E., et al.
Impact Factor: 4.13
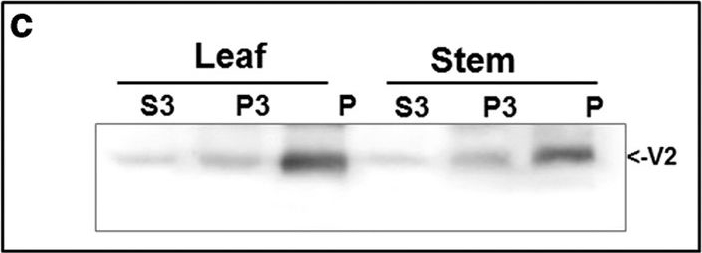
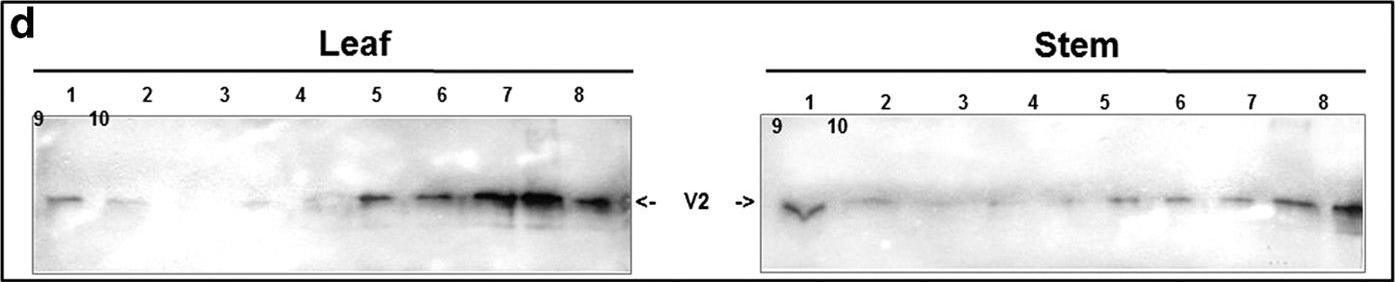
Open PublicationDetection of TYLCV V2 in tomato leaf and stem 28 and 49 days (dpi) after infection. a: western blot of V2 and OE33 (chloroplast protein used as an internal marker). b: western blot of V2 in leaf and stem tissues at 49 dpi fractioned into cytoplasmic/membrane (Cyt) and nuclear (N) components; cytoplasmic Hsp70 and nuclear histone H3 used as internal markers to assess the fraction purity. c: western blot of V2 in leaf and stem tissues of 49 dpi fractionated into insoluble debris and cell wall (P), 3000?g pellet (P3) and soluble protein (S3). d: western blot analysis of V2, distributed in linear 10-50% sucrose gradients from leaf and stem native protein extracts at 49 dpi; gradients were divided into 10 fractions, 1 (top) to 10 (bottom) and aliquots were subjected to SDS-PAGE.
Reactant: Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato)
Application: Western Blotting
Pudmed ID: 25940862
Journal: Sci Rep
Figure Number: 1B
Published Date: 2015-05-05
First Author: Moshe, A., Belausov, E., et al.
Impact Factor: 4.13
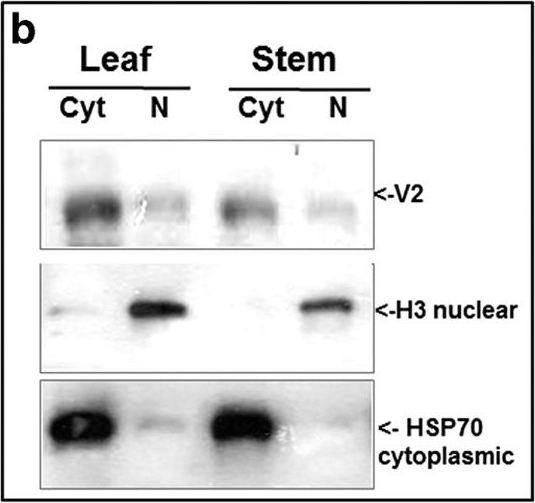
Open PublicationDetection of TYLCV V2 in tomato leaf and stem 28 and 49 days (dpi) after infection. a: western blot of V2 and OE33 (chloroplast protein used as an internal marker). b: western blot of V2 in leaf and stem tissues at 49 dpi fractioned into cytoplasmic/membrane (Cyt) and nuclear (N) components; cytoplasmic Hsp70 and nuclear histone H3 used as internal markers to assess the fraction purity. c: western blot of V2 in leaf and stem tissues of 49 dpi fractionated into insoluble debris and cell wall (P), 3000?g pellet (P3) and soluble protein (S3). d: western blot analysis of V2, distributed in linear 10-50% sucrose gradients from leaf and stem native protein extracts at 49 dpi; gradients were divided into 10 fractions, 1 (top) to 10 (bottom) and aliquots were subjected to SDS-PAGE.
Reactant: Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato)
Application: Western Blotting
Pudmed ID: 25940862
Journal: Sci Rep
Figure Number: 1C
Published Date: 2015-05-05
First Author: Moshe, A., Belausov, E., et al.
Impact Factor: 4.13
Open PublicationDetection of TYLCV V2 in tomato leaf and stem 28 and 49 days (dpi) after infection. a: western blot of V2 and OE33 (chloroplast protein used as an internal marker). b: western blot of V2 in leaf and stem tissues at 49 dpi fractioned into cytoplasmic/membrane (Cyt) and nuclear (N) components; cytoplasmic Hsp70 and nuclear histone H3 used as internal markers to assess the fraction purity. c: western blot of V2 in leaf and stem tissues of 49 dpi fractionated into insoluble debris and cell wall (P), 3000?g pellet (P3) and soluble protein (S3). d: western blot analysis of V2, distributed in linear 10-50% sucrose gradients from leaf and stem native protein extracts at 49 dpi; gradients were divided into 10 fractions, 1 (top) to 10 (bottom) and aliquots were subjected to SDS-PAGE.
Reactant: Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato)
Application: Western Blotting
Pudmed ID: 25940862
Journal: Sci Rep
Figure Number: 1D
Published Date: 2015-05-05
First Author: Moshe, A., Belausov, E., et al.
Impact Factor: 4.13
Open PublicationDetection of TYLCV V2 in tomato leaf and stem 28 and 49 days (dpi) after infection. a: western blot of V2 and OE33 (chloroplast protein used as an internal marker). b: western blot of V2 in leaf and stem tissues at 49 dpi fractioned into cytoplasmic/membrane (Cyt) and nuclear (N) components; cytoplasmic Hsp70 and nuclear histone H3 used as internal markers to assess the fraction purity. c: western blot of V2 in leaf and stem tissues of 49 dpi fractionated into insoluble debris and cell wall (P), 3000?g pellet (P3) and soluble protein (S3). d: western blot analysis of V2, distributed in linear 10-50% sucrose gradients from leaf and stem native protein extracts at 49 dpi; gradients were divided into 10 fractions, 1 (top) to 10 (bottom) and aliquots were subjected to SDS-PAGE.
Reactant: Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato)
Application: Western Blotting
Pudmed ID: 25940862
Journal: Sci Rep
Figure Number: 3A
Published Date: 2015-05-05
First Author: Moshe, A., Belausov, E., et al.
Impact Factor: 4.13
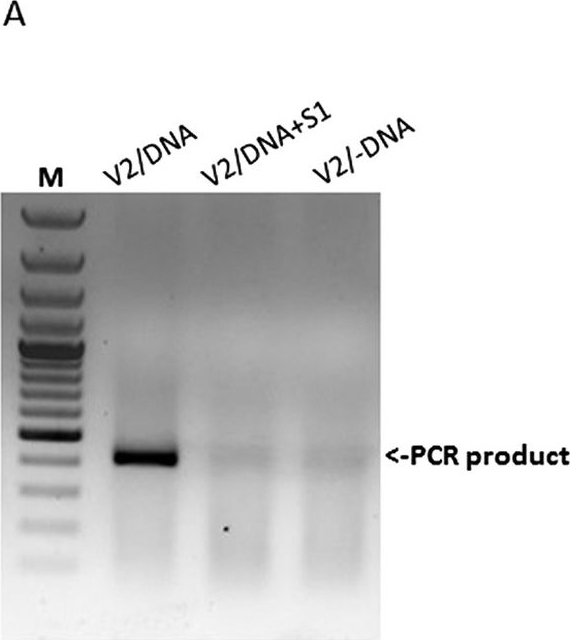
Open PublicationV2 forms complexes with TYLCV genomic DNA. Detection of TYLCV DNA-V2 complexes in vitro (a) and in planta (b). a: PCR detection of viral DNA following immuno-capture with V2 antibody of mixtures of V2 and infected plant DNA; V2/DNA: V2 incubated with untreated DNA, V2/DNA?+?S1: V2 incubated with DNA treated with S1 nuclease, V2/-DNA: V2 incubated without DNA. M - 100 bp DNA marker. b: Southern blot analysis of viral DNA-V2 complexes from infected tomato plants; DNA: DNA from infected plants, V2/DNA: DNA extracted from immunoprecipitated V2 complexes, V2/DNA?+?S1: DNA extracted from immunoprecipitated V2 complexes and treated with S1 nuclease.
- Additional Information
-
Additional information (application): This antibody is detecting recombinant TYLCV V2 protein - Background
-
Background: TYLCV CP (Tomato yellow leaf curl virus coat protein V2) accumulates in tomato leaves during infection. This protein was detected in the phloem of associated cells. TYLCV virus attacts tomato cultures worldwide and is transmitted by the white flye Bemisia tabaci.
- Product Citations
-
Selected references: Moshe et al. (2015). The Tomato yellow leaf curl virus V2 protein forms aggregates depending on the cytoskeleton integrity and binds viral genomic DNA. Sci Rep. 2015 May 5;5:9967. doi: 10.1038/srep09967. - Protocols
-
- Reviews:
-
This product doesn't have any reviews.
Accessories

AS15 3055 | Clonality: Polyclonal | Host: Rabbit | Reactivity: Tomato yellow leaf curl virus coat protein

AS15 3058 | Clonality: Polyclonal | Host: Rabbit | Reactivity: Tomato yellow leaf curl virus coat protein C4