1
Anti-BAK1 | Brassinosteroid insensitive 1-associated receptor kinase 1
AS12 1858 | Clonality: Polyclonal | Host: Rabbit | Reactivity: Arabidopsis thaliana, Solanum lycopersicum
- Product Info
-
Immunogen: KLH-conjugated peptide, chosen from Arabidopsis thaliana Bak1 sequence, TAIR: AT4G33430 UniProt: Q94F62 Host: Rabbit Clonality: Polyclonal Purity: Immunogen affinity purified serum in PBS pH 7.4. Format: Lyophilized Quantity: 50 µg Reconstitution: For reconstitution add 50 µl of sterile water Storage: Store lyophilized/reconstituted at -20°C; once reconstituted make aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles,Please remember to spin the tubes briefly prior to opening them to avoid any losses that might occur from material adhering to the cap or sides of the tube. Tested applications: Immunoprecipitation (IP), Western blot (WB) Recommended dilution: 2 µl/50 µl of Protein G agarose, 1 : 5000 (WB) Expected | apparent MW: 68 | 70 kDa
- Reactivity
-
Confirmed reactivity: Arabidopsis thaliana, Solanum lycopersicum Predicted reactivity: Thelungiella halophila
Species of your interest not listed? Contact usNot reactive in: Hordeum vulgare, Lactuca sativa, Nicotiana benthamiana, Oryza sativa
- Application Examples
-
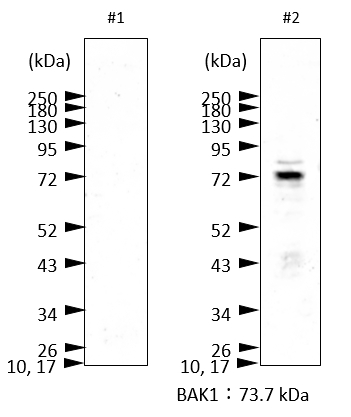
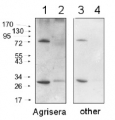
Example of how proper protein extraction contributes to detection of a target band of BAK1
Protein extraction methods
#1 Approximately 100 mg of plant material were extracted in 0.2 ml of homogenization buffer (0.1 M EDTA, 0.12 M Tris-HCl, pH6.8, 4% SDS, 10% glycerol, 10% 2-mercaptoethanol) with a pistil and a small amount of sand in an 1.5ml Eppendorf tube. Another 0.8 ml of buffer were added and the extract was mixed thoroughly. Debris was pelleted by centrifugation at 14,000 rpm. The supernatant was mixed with 2x SDS loading buffer and boiled at 95°C for 10min. (no BAK1 band detected)
#2 Approximately 200 mg of plant material were grounded in a mortar with liquid nitrogen and collected into 2.0 mL microtube. After adding 0.2 ml of 2x SDS loading buffer (0.125M Tris-HCl (pH 6.8), 10% 2-Mercaptoethanol, 4% SDS, 10% Sucrose, 0.004% BPB), the samples was mixed by vortex for 2min and boiled at at 95°C for 10min. Debris was pelleted by centrifugation at 14,000 rpm. The supernatant was collected. (BAK1 band visualized)
Western blot procedure
30 microL were separated on 10% SDS-PAGE and blotted 7min to Trans-Blot Turbo Mini PVDF Transfer Packs using Trans-Blot Turbo Transfer System (Bio-Rad). Blot was blocked with 4% milk in TBS-T for 1h/RT with agitation. Blot was incubated in the primary antibody at a dilution of 1: 2000 in 4% milk in TBS-T for 1h/RT with agitation. The antibody solution was decanted and the blot was washed 3 times for 5 min in TBS-T at RT with agitation. Blot was incubated in Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H&L), HRP conjugated (AS09 602 Agrisera), 1: 2000 1h/RT with agitation. The blot was washed 3 times for 15 min in TBS-T at RT with agitation and developed for 5 min with AgriseraECL SuperBright. Exposure time was 1min.
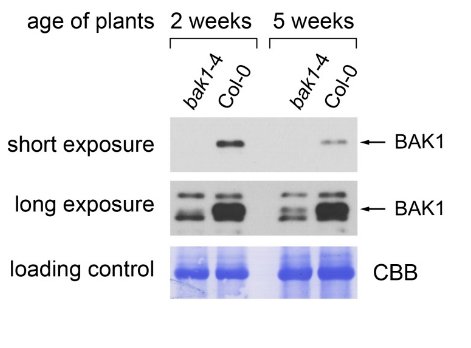
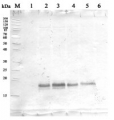
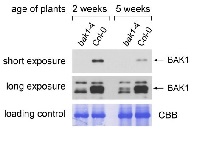
Plant material: Arabidopsis thaliana Col-0 (wild type) bak1-4 (knock-out mutant for BAK1, does not show any full-length BAK1 transcript, Kemmerling et al., 2007). Method: Two-week-old seedlings and leaf material of 5-week-old plants (grown under short day conditions, 8h light) were collected and frozen in liquid nitrogen. Approximately 100 mg of plant material were extracted in 0.2 ml of homogenization buffer (250 mM sucrose, 50 mM HEPES-KOH pH 7.5, 0.5% Triton X-100, 5% glycerol, 50 mM Na4P2O7, 1 mM Na2MoO4, 25 mM NaF, 2 mM DTT, Sigma plant protease inhibitor cocktail) with a glass pistil and a small amount of sand in an 1.5ml Eppendorf tube. Another 0.8 ml of buffer were added and the extract was mixed thoroughly. Debris was pelleted by centrifugation in a table-top microcentrifuge at 13 000 rpm. The supernatant was mixed with 4x SDS loading buffer (200 mM TRIS-HCl pH 6.8, 400 mM DTT, 8% SDS, 40% glycerol, 0.1% bromophenol blue) and boiled at 95°C for 5min. 10µl were run on an 10% polyacrylamide gel and blotted onto a 0.45µm PVDF membrane (Carl Roth). The membrane was blocked for 1h in TBS-T (150mM NaCl, 10mM Tris-HCl pH8, 0.05% Tween-20) containing 5% skimmed milk powder. The primary antibody (Agrisera Rabbit anti-BAK1, AS12 1858, 1µg/µl) was diluted 1:5000 in TBS-T containing 5% milk powder and incubated on the membrane overnight at 4°C. Then the membrane was washed 5 times 15min with TBS-T containing 5% milk powder. The secondary antibody (Agrisera Goat anti-rabbit IgG (H&L) HRP conjugate, AS09 602, 0.91 µg/µl) was diluted 1:5000 in the same solution and incubated on the membrane at room temperature for 2h. The membrane was then washed 5 times 15min with TBS-T (no milk powder) and the blot was developed using chemiluminescent detection reagent. Short exposure: 1 minute. Long exposure: 10 minutes.
Courtesy of Dr. Elena Petusching, Georg-August-University Goettingen, GermanyApplication examples: 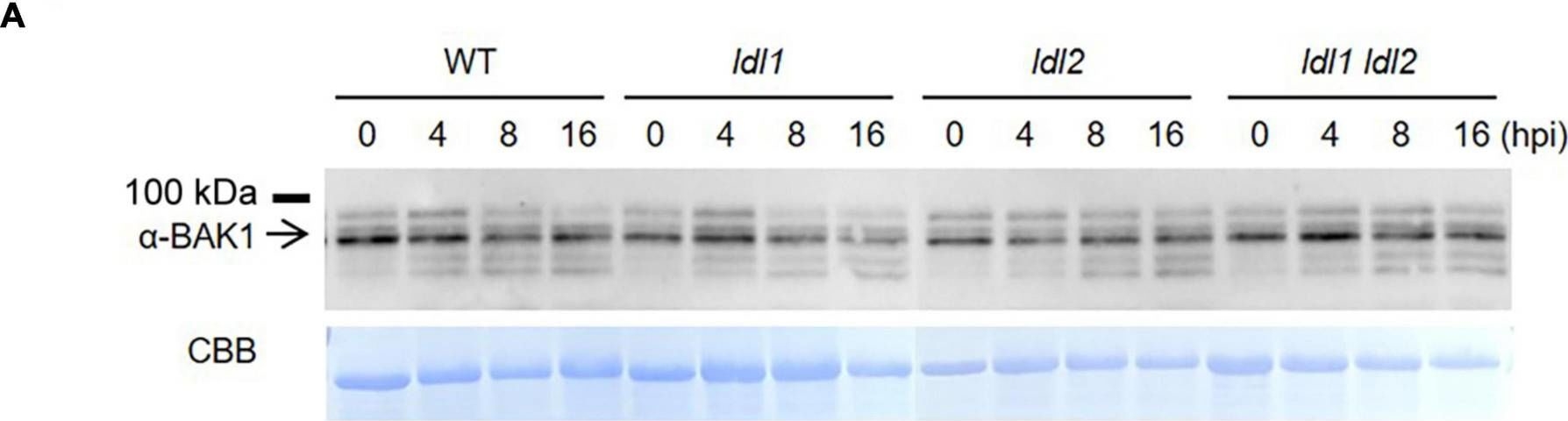
Reactant: Arabidopsis thaliana (Thale cress)
Application: Western Blotting
Pudmed ID: 34194459
Journal: Front Plant Sci
Figure Number: 3A
Published Date: 2021-07-02
First Author: Noh, S. W., Seo, R. R., et al.
Impact Factor: 5.435
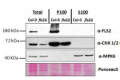
Open PublicationTranscript levels of MAMP-responsive genes increase in ldl mutants after Pseudomonas infection. (A) BAK1 protein abundance in WT, ldl1, ldl2, and ldl1 ldl2 during PstDC3000 infection (OD600 = 0.01). (B) Callose deposition in Arabidopsis leaves infiltrated with PstDC3000 at 24 h post-inoculation (hpi). Equivalent volumes of 10 m MgSO4 were used for mock conditions. Left panel: representative portions of leaves from WT, ldl1, ldl2, and ldl1 ldl2 plants stained with aniline blue to visualize deposited callose. Right panel: average ± SD of the number of callose deposits per field (n = 10) (Scale bars are 300 ?m). No significant differences from WT plants were observed when analyzed with a one-way ANOVA-Tukey test (p < 0.05). (C) Transcript levels of FRK1, NHL10, and At1g51890 in local leaves of WT, ldl1, ldl2, and ldl1 ldl2 plants at 0, 8, and 16 hpi with PstDC3000 (OD600 = 0.01). Bar indicates the SD (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, two-tailed Student’s t-test, n = 3). The experiments were repeated 4 times; the numerators of the fractions below each plot indicate the number of trials showing differences from WT plants.
- Additional Information
-
Additional information: Antibodies bind to AtBAK1-Myc. They do not cross react with AtSOBIR.
This product can be sold containing proclin if requested.Additional information (application): Extra Information on CE extraction buffer: CE buffer does not need to be made freshly everytime. Aliquots can be kept at -20°C. Na2MoO4 and NaF are phosphatase inhibitors, included to prevent lose phosphorylation form our protein of interest during extraction. EDTA chelates metal ions and thus inhibits many enzymes which need metal ions as co-factors and inhibits the action of proteases. Protease inhibitor coctail is Sigma product number P 9599 which is used in dilution 1: 100.
Antibody is reconizing AtBAK1-Myc in total extracts. - Background
-
Background: BAK1 (Brassinosteroid insensitive 1-associated receptor kinase 1) controls expression of genes associated with innate immunity in the absence of pathogens or elicitors. Phosphorylated Brl1. Involved in programmed cell death (PCD). Subcellular localization: cell membrane. Alternative names: BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE 1-associated receptor kinase 1, BAK1, BRI1-ASSOCIATED RECEPTOR KINASE, RKS10, RECEPTOR KINASES LIKE SERK 10, SERK3, SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE 3, ELG, ELONGATED, ATSERK3, SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE 3, ATBAK1.
- Product Citations
-
Selected references: Bierman et al. (2025). A RALF-brassinosteroid signaling circuit regulates Arabidopsis hypocotyl cell shape. Curr Biol. 2025 Sep 26:S0960-9822(25)01186-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2025.09.016.
Lee et al. (2024). Reprogramming of flagellin receptor responses with surrogate ligands. Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 12;15(1):9811.doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54271-5.
Jing et al. (2024). Copine proteins are required for brassinosteroid signaling in maize and Arabidopsis. Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 8;15(1):2028.doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46289-6.
Xu et al. (2022) The Phloem Intercalated With Xylem-Correlated 3 Receptor-Like Kinase Constitutively Interacts With Brassinosteroid Insensitive 1-Associated Receptor Kinase 1 and Is Involved in Vascular Development in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jan 11;12:706633. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.706633. PMID: 35087541; PMCID: PMC8786740.
Kalischuk et al. (2022) Amplification of cell signaling and disease resistance by an immunity receptor Ve1Ve2 heterocomplex in plants. Commun Biol. 2022 May 25;5(1):497. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03439-0. PMID: 35614138; PMCID: PMC9132969.
Katarzyna Parys et al (2021) Signatures of antagonistic pleiotropy in a bacterial flagellin epitope,Cell Host & Microbe,Volume 29, Issue 4,2021,Pages 620-634.e9,ISSN 1931-3128,https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2021.02.008.(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1931312821000871)
Zhang et al. (2019). An important role of L -fucose biosynthesis and protein fucosylation genes in Arabidopsis immunity. New Phytol. 2018 Dec 15. doi: 10.1111/nph.15639.
Hu et al. (2018). A group of receptor kinases are essential for CLAVATA signalling to maintain stem cell homeostasis. Nat Plants. 2018 Apr;4(4):205-211. doi: 10.1038/s41477-018-0123-z. (CoIP) - Protocols
-
Agrisera Western Blot protocol and video tutorials
Protocols to work with plant and algal protein extracts
Oxygenic photosynthesis poster by prof. Govindjee and Dr. Shevela
Z-scheme of photosynthetic electron transport by prof. Govindjee and Dr. Björn and Dr. Shevela - Reviews:
-
Leon | 2021-08-11This product works very well for our experiments.elwira smakowska | 2019-11-19I have used this antibody for a multiple experiments:
- WB from the crude Arabidopsis extract
-WB on the PM fraction from Arabidopsis
-coIP from N.benthamiana
-coIP from Arabodopsis
For all mentioned above i was always getting a very satisfactory results! Great specificity! thank you Agrisera!Lirong Zeng | 2018-09-21Worked well for our experiments.Elena Shpak | 2017-01-18We used this antibody for Western with crude microsomal fractions from young Arabidopsis seedlings at a dilution 5