1
Anti-Xyloglucan (monoclonal, clone LM15)
From the laboratory of Paul Knox, Phd, University of Leeds, United Kingdom
- Product Info
-
Sub class: IgG2c Immunogen: Neoglycoprotein, Xyloglucan Host: Rat Clonality: Monoclonal Purity: Cell culture supernatant. Format: Liquid Quantity: 1 ml Storage: Store at +4°C (short term) and at -20°C (long term). Tested applications: ELISA (ELISA), Immuniflourescence (IF) Recommended dilution: 1:10 (ELISA, IF) - Reactivity
-
Confirmed reactivity: Higher plants, ferns and mosses Not reactive in: No confirmed exceptions from predicted reactivity are currently known - Additional Information
-
Additional information: Contains 0.05% Sodium Azide
Reacts with the XXXG motif of land plants xyloglucan.
This antibody is directed toward the nonreducing end, with the requirement for the second to last Glc to be substituted with an a-1,6-linked Xyl Ruprecht et al. (2017). - Background
-
Background: The plant cell wall surrounds the plant cell as a complex network of polysaccharides classed as: cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectic polysaccharides and glycoproteins. Anchored to or embedded into plant cell wall are other polymers, like: lignin, suberin or cutin. Xyloglucan is a hemiceullose or polysaccharide that can be found in the primary cell wall. - Product Citations
-
Selected references: Jacquer et al. (2025). A developmental switch controls cell-to-cell transport in roots via pectin-linked plasmodesmata changes. Mol Plant . 2025 Jul 17:S1674-2052(25)00233-3. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2025.07.004.
Ruprecht et al. (2017). A Synthetic Glycan Microarray Enables Epitope Mapping of Plant Cell Wall Glycan-Directed Antibodies. Plant Physiol. 2017 Nov;175(3):1094-1104. doi: 10.1104/pp.17.00737. - Protocols
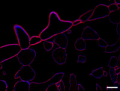
- Immunofluorsecence as described in: Developmental complexity of arabinan polysaccharides and their processing in plant cell walls Verhertbruggen Y, Marcus SE, Haeger A, Verhoef R, Schols HA, McCleary BV, McKee L, Gilbert HJ, Knox JP., The Plant Journal (2009) 59, 413–425.
- Reviews:
-
This product doesn't have any reviews.
Accessories
From the laboratory of Paul Knox, Phd, University of Leeds, United Kingdom
From the laboratory of Paul Knox, Phd, University of Leeds, United Kingdom