1

Anti-GS | Glutathione synthase, GSH-S
AS06 183 | Clonality: Polyclonal | Host: Rabbit | Reactivity: Brassica campestris, Nicotiana tabacum, Phaeodactylum tricornutum, Solanum lycopersicum, Zea mays
- Product Info
-
Immunogen: KLH-conjugated synthetic peptide derived from Zea mays GSH-S sequence Q8W4W2
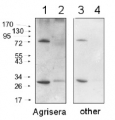
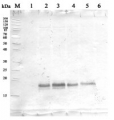
Host: Rabbit Clonality: Polyclonal Purity: Total IgG. Protein G purified in PBS pH 7.4. Format: Lyophilized Quantity: 100 µl Reconstitution: For reconstitution add 100 µl of sterile water Storage: Store lyophilized/reconstituted at -20°C; once reconstituted make aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Please remember to spin the tubes briefly prior to opening them to avoid any losses that might occur from material adhering to the cap or sides of the tube. Tested applications: Immunolocalization (IL), Western blot (WB) Recommended dilution: 1 : 2000 (WB) Expected | apparent MW: 45 kDa
- Reactivity
-
Confirmed reactivity: Brassica campestris, Nicotiana tabacum, Oryza sativa, Phaeodactylum tricornutum, Solanum lycopersicum, Zea mays Predicted reactivity: Aegilops tauschii, Arabidopsis thaliana, Arundo donax, Asparagus officinalis, Brachypodium distachyon, Capsicum annuum, Cicer arietinum, Citrus clementina, Corchorus olitorius, Cucumis sativus, Daucus carota subsp. sativus, Dimocarpus longan, Eucalyptus grandis, Gossypium hirsutum , Helianthus annuus , Hevea brasiliensis, Hordeum vulgare, Jatropha curcas, Lotus japonicus, Lupinus angustifolius, Lycium chinense, Musa acuminata, Nelumbo nucifera, Nicotiana tabacum, Nicotiana sylvestris, Pisum sativum, Setaria italica, Sorghum bicolor, Spinacia oleracea, Triticum aestivum, Zostera marina, Vitis vinifera
Species of your interest not listed? Contact usNot reactive in: Galdieria sulphuraria - Additional Information
-
Additional information: Total IgG concentration is 3,7 µg/µl Additional information (application): Immunolocalization has been done for Arabidopsis thaliana and Nicotiana tabacum
- Background
-
Background: Glutathione synthetase (GSH-S) catalyses the last step of glutathione (GSH) synthesis. GSH is synthesized in two ATP-dependent steps: in the first, gamma-glutamylcysteine (gamma-EC) is synthesized from L-glutamate and cysteine, catalyzed by gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase (g-ECS); in the second step, catalysed by GSH-S, glycine is added to the C-terminal end of gamma-EC. GSH is the predominant non-protein thiol in all nearly where it acts as an antioxidant in stress responses and as a mobile pool of reduced sulfur. It is also important in the regulation of plant growth and development
- Product Citations
-
Selected references: Sun et a. (2019). Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of the Molecular Mechanism of the Hairy Roots of Brassica campestris L. in Response to Cadmium Stress. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 26;21(1). pii: E180. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010180.
Jayawardena et al. (2016). Elevated CO2 plus chronic warming reduces nitrogen uptake and levels or activities of nitrogen -uptake and -assimilatory proteins in tomato roots. Physiol Plant. 2016 Nov 28. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12532. [Epub ahead of print]
Baojian et al. (2014). Maize (Zea mays L.) seedling leaf nuclear proteome and differentially expressed proteins between a hybrid and its parental lines. Proteomics, DOI: 10.1002/pmic.201300147.
Gomez et al. (2004) Intercellular distribution of glutathione synthesis in maize leaves and its response to short term chilling. Plant Physiol. 134: 1662-1671. - Protocols
-
Agrisera Western Blot protocol and video tutorials
Protocols to work with plant and algal protein extracts - Reviews:
-
This product doesn't have any reviews.
Accessories
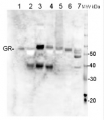
AS06 181 | Clonality: Polyclonal | Host: Rabbit | Reactivity: Arabidopsis thaliana, Catharanthus roseus,Glycine max, Hordeum vulgare, Medicago sativa, Nicotiana tabacum, Oryza sativa, Pisum sativum, Salicornia sp., Silene vulgaris, Scenedesmus quadricauda (algae), Solanum tuberosum, Zea mays