1

Anti-NifH | Nitrogenase iron protein
AS01 021A | Clonality: Polyclonal | Host: Hen | Reactivity: [global antibody] for bacteria
Benefits of using this antibody
- Product Info
-
Immunogen: KLH-conjugated synthetic peptide derived from known bacterial NifH subunits of bacterial nitrogenase enzymes of the FeMoCo type including Synechoccocus sp. Q2JP78 , Trichodesmium theibautii, Anabaena sp. P33178 and Nostoc sp. Q51296
Host: Chicken Clonality: Polyclonal Purity: Immunogen affinity purified IgY in PBS pH 8 and 0.02 % sodium azide. Format: Liquid at 1.28 mg/ml Quantity: 100 µg Storage: Store at 4°C; make aliquots to avoid working with a stock. Please remember to spin the tubes briefly prior to opening them to avoid any losses that might occur from material adhering to the cap or sides of the tube. Tested applications: Immunofluorescence (IF), Immunohistochemistry (IHC), Western blot (WB) Recommended dilution: 1 : 500 (IHC), 6 µg/ml (IF), 1 : 2000 (WB) Expected | apparent MW: 27 | 32.5 kDa - Reactivity
-
Confirmed reactivity: Anabaena PCC7120, Clostridium butyricum, Codakia orbicularis, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii CS-505, Dolichospermum sp., Methylosinus sp., Nostoc sp, Rhodopseudomonas palustris, Trichodesmium sp., nodules of Trifolium repens L., Vibrio natriegens ATCC 14048 Predicted reactivity: Azotobacter vinelandii (Gram-), Bradyrhizobium japonicum, Cyanobacteria, Cyanothece ATCC51142, Desulfotomaculum reducens (strain MI-1),Clostridium cellobioparum, Enterobacter , genera, euryachaeotes, Klebsiella pneumonia, Magnetococcus sp., Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum, Methanococcus maripaludis, Methylobacterium sp., Mesoorhizobium loti, Rhodopseudomonas palustris TIE-1 strain, alpha,gamma,beta proteobacteria, enterobacteria, low GC gram+, high GC gram +, able to fix atmoshperic nitrogen, Rhizobium meliloti
Species of your interest not listed? Contact usNot reactive in: Synechococcus sp. PCC 7942 and Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 as NifH protein is not present in those cyanobacterial species, Frankia sp.
- Application Examples
-
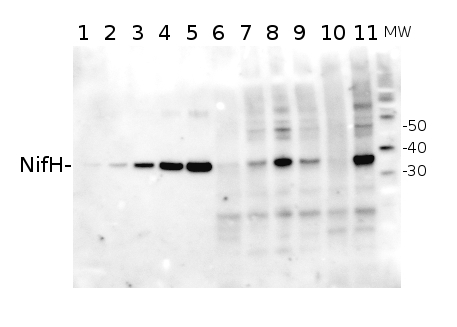
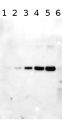
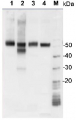
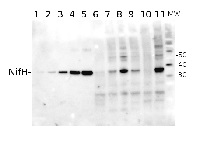
Total Trichodesmium sp. protein extract (lanes 6-11, 80 pmol chlorophyll loaded) extracted with PEB (AS08 300), and NifH protein standard (lanes 1-5, 0.05, 0.1, 0.3 0.75 and 1.5 pmol standard loaded) were separated on 4-12% NuPage (Invitrogen) LDS-PAGE and blotted 1h to PVDF. Blots were blocked immediately following transfer in 2% blocking reagent in 20 mM Tris, 137 mM sodium chloride pH 7.6 with 0.1% (v/v) Tween-20 (TBS-T) for 1h at room temperature with agitation. Blots were incubated in the primary antibody at a dilution of 1:40 000 for 1h at room temperature with agitation. The antibody solution was decanted and the blot was rinsed briefly twice, then washed once for 15 min and 3 times for 5 min in TBS-T at room temperature with agitation. Blots were incubated in secondary antibody (anti-hen IgY horse radish peroxidase conjugated) diluted to 1:50 000 in 2% blocking solution for 1h at room temperature with agitation. The blots were washed as above and developed for 5 min with chemiluminescent detection reagent according the manufacturers instructions. Images of the blots were obtained using a CCD imager (FluorSMax, Bio-Rad) and Quantity One software (Bio-Rad).
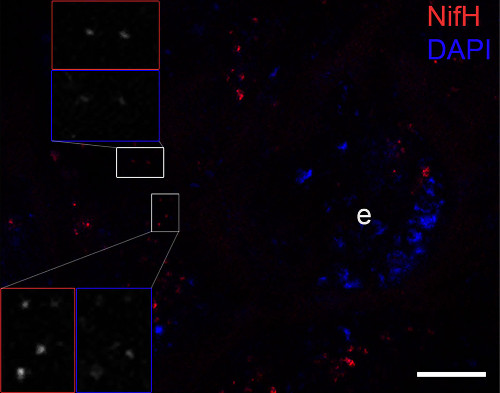 Immunofluorescence image confirming the NifH protein (bright red dots) close to the cuticle of the ileum and covering or being directly adjacent to the bacterial DNA signals (blue dots: stained by DAPI). The host DNA of the epithelium (e) was also visible. The inset frames show magnifications of red stained dots representing NifH and DAPI signals. Scale bar is10 µm.Courtesy of Dr. Panagiotis Sapountzis, Center for Social Evolution University of Copenhagen, Danmark
Immunofluorescence image confirming the NifH protein (bright red dots) close to the cuticle of the ileum and covering or being directly adjacent to the bacterial DNA signals (blue dots: stained by DAPI). The host DNA of the epithelium (e) was also visible. The inset frames show magnifications of red stained dots representing NifH and DAPI signals. Scale bar is10 µm.Courtesy of Dr. Panagiotis Sapountzis, Center for Social Evolution University of Copenhagen, DanmarkApplication examples: 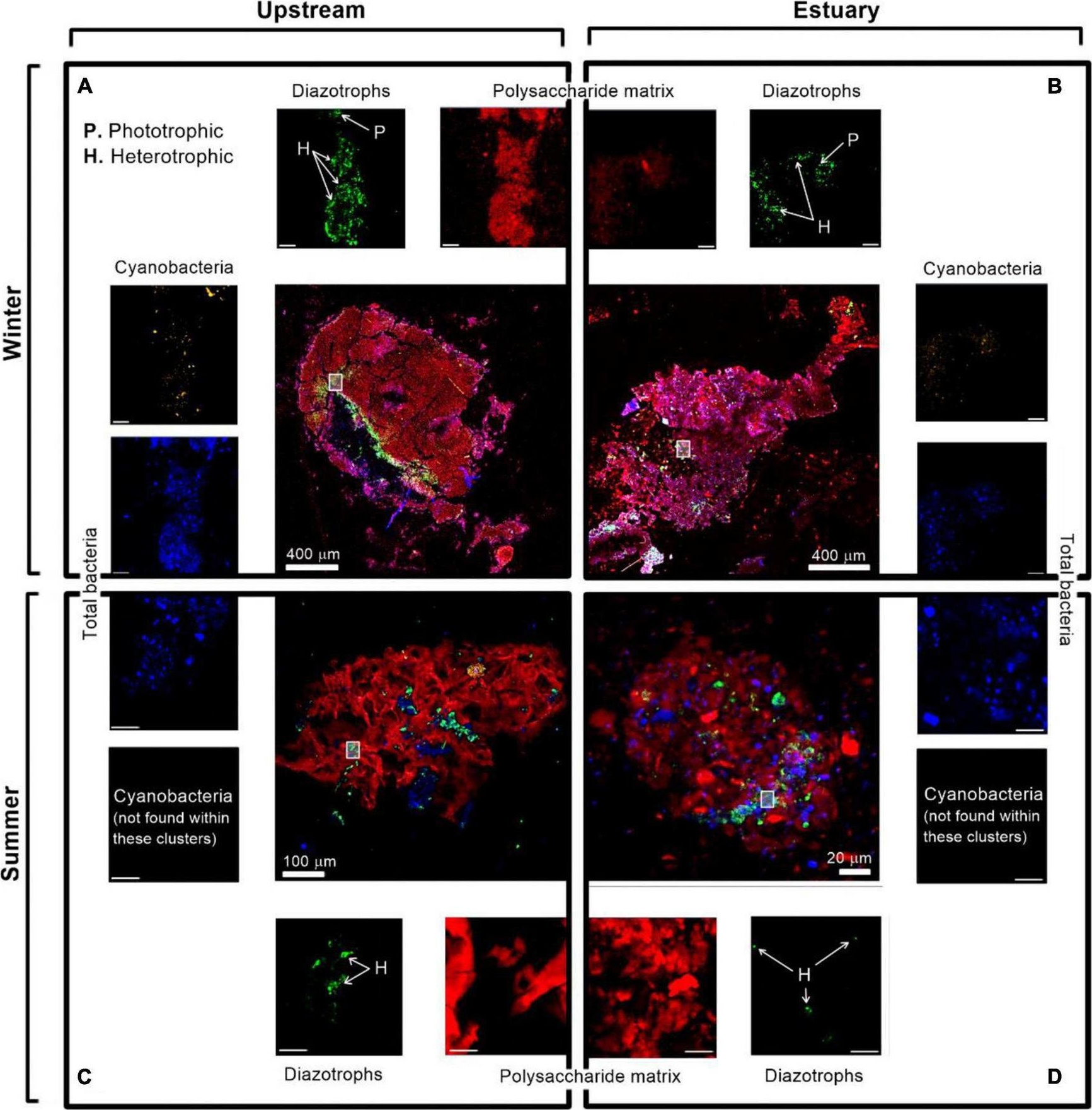
Reactant: Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Application: Immunocytochemistry-immunofluorescence
Pudmed ID: 35237246
Journal: Front Microbiol
Figure Number: 7A
Published Date: 2022-03-04
First Author: Bar-Zeev, E.
Impact Factor: 5.585
Open PublicationImmunolabeling micrograph images of diazotrophs associated with aggregates collected from the Qishon River (A,C - stream; B,D - Estuary) during the winter (top panels) and summer time (bottom panels). Images were captured by a confocal laser scanning microscope with a double close-up of bacteria associated with aggregates. Images were taken in four layers (sub-plots around each aggregate) as cyanobacteria by autofluorescence of the phycoerythrin pigment (orange/white), diazotrophs by immunolabeling of nitrogenase [green, bacteria by DAPI (blue), and polysaccharides by ConA (red). The mark on the aggregates represents a close-up of the image. The reported scale bar in the top inserts is 10 μm, while the scale bar in the bottom inserts is 5 μm. H refers to heterotrophic diazotrophs and P to phototrophic diazotrophs, distinguished by the phycoerythrin pigment]. Additional microscopy images are provided in the Supplementary Figure 1.
- Additional Information
-
Additional information (application): An enzyme involved in chlorophyll synthesis, present in all cyanobacteria (fixing and non-nitrogen fixing) is a member of the NifH family/superfamily. Agrisera anti-NifH antibody will not show a strong reactivity to this target.
In photobionts like Anabaena sp., low nitrate growth is required to turn on the NifH expression to high enough levels to detect NifH protein.
Immunofluorescence protocol
Insect dissected tissues (digestive tract, fat body, carrying NifH positive bacteria) of large workers were fixed in cold methanol (20 min, -20°C) and then permeabilized in cold acetone (5 min, -20°C). Samples were subsequently rinsed three times with PBS with 0.1 % Triton-X 100 at RT (PBST) and incubated for 5 minutes in PBST. This was followed by incubation of tissues for 1 hr with 6 ug/ml affinity purified anti-NifH antibody (Agrisera, AS01 021A) diluted in PBS-TBSA (PBS, 0.1 % v/v Triton-X-100, 1 mg/ml BSA) and 3 washings with PBST. Samples were then incubated in the dark with a goat anti-chicken IgY conjugated to Dylight 488 (Pierce, SA5-10070) for 45 min and were washed twice (PBS, 0.1%v/v Triton-X-100). Finally, the tissues were mounted in Vectashield medium containing DAPI (Vector Laboratories, H-1500) and viewed under a SP5 Leica confocal microscope with 10X and 63X objectives.
Courtesy of Drs. Panagiotis Sapountzis and Mariya Zhukova, University of Copenhagen, Danmark - Background
-
Background: Nitrogenase is involved in biological fixation of atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia. Alternative protein names: nitrogenase component II, nitrogenase Fe protein, nitrogenase reductase, FeMoCo-nitrogenase.
- Product Citations
-
Selected references: Abdela et al. (2025). Transcription of Nitrogen Fixation Genes Is Enhanced at Unfavorably High Oxygen Concentrations for Diazotrophic Growth in a Methane oxidizing Bacterium. Microbes Environ . 2025;40(4). doi: 10.1264/jsme2.ME25032.
Han et al. (2025). Nitrogen stable isotope fractionation by biological nitrogen fixation reveals cellular nitrogenase is diffusion limited.PNAS NEXUS, Feb 2025, doi.org/10.1093/pnasnexus/pgaf061.
Zhou et al. (2024). Inorganic nitrogen inhibits symbiotic nitrogen fixation through blocking NRAMP2- mediated iron delivery in soybean nodules. Nat Commun . 2024 Oct 17;15(1):8946. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53325-y.
Wen et al. (2024). Effects of CO2 on the nitrogen isotopic composition of marine diazotrophic cyanobacteria. Geophysical Research Letters.
Ito et al. (2024). Improvement of the nitrogenase activity in Escherichia coli that expresses the nitrogen fixation-related genes from Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024 Jul 3:728:150345.doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.150345.
Yadav et al.(2023) Occurrence, identification and characterization of diazotrophic bacteria from aerial roots of Rhynchostylis retusa (L.) Blume for plant growth-promoting activity. Arch Microbiol. 2023 Mar 22;205(4):131. doi: 10.1007/s00203-023-03458-3.
Fernández-Juárez et al. (2023), Biofilm formation and cell plasticity drive diazotrophy in an anoxygenic phototrophic bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Nov ;89(11):e0102723. doi: 10.1128/aem.01027-23.
Santana-Sanchez, et al. (2023) Flv3A facilitates O2 photoreduction and affects H2 photoproduction independently of Flv1A in diazotrophic Anabaena filaments. New Phytol. 2023;237(1):126-139. doi:10.1111/nph.18506
Chen et al. (2022) Exogenous hydrogen sulphide alleviates nodule senescence in Glycine max-Sinorhizobium fredii symbiotic system, Preprint from Research Square, 22 Jul 2022, DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-1752770/v1
Li et al. (2022), The effects of Ni availability on H2 production and N2 fixation in a model unicellular diazotroph: The expression of hydrogenase and nitrogenase. Limnol Oceanogr, 67: 1566-1576. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.12151
He et al. (2021) Vegetative cells may perform nitrogen fixation function under nitrogen deprivation in Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 based on genome-wide differential expression analysis. PLoS One. 2021 Mar 4;16(3):e0248155. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248155. PMID: 33662009; PMCID: PMC7932525. (Immunolocalization)
Liu et al. (2020). A VIT-like transporter facilitates iron transport into nodule symbiosomes for nitrogen fixation in soybean. New Phytol . 2020 Mar 2. doi: 10.1111/nph.16506.
Geisler et al. (2019). Direct Detection of Heterotrophic Diazotrophs Associated with Planktonic Aggregates. Sci Rep. 2019 Jun 26;9(1):9288. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45505-4. (immunolocalization).
Murukesan et al. (2019). Acclimation responses of immobilized N2-fixing heterocystous cyanobacteria to long-term H2 photoproduction conditions: carbon allocation, oxidative stress and carotenoid production. J Appl Phycol (2019) 31: 131.
Konig et al. (2016). Nitrogen fixation in a chemoautotrophic lucinid symbiosis. Nat Microbiol. 2016 Oct 24;2:16193. doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.193.
Liberti et al. (2015). Bacterial symbiont sharing in Megalomyrmex social parasites and their fungus-growing ant hosts. Mol Ecol. 2015 Apr 24. doi: 10.1111/mec.13216.
Calusinska et al. (2015). Genome-wide transcriptional analysis suggests hydrogenase- and nitrogenase-mediated hydrogen production in Clostridium butyricum CWBI 1009. Biotechnology for Biofuels (2015) 8:27.
Moirangthem et al. (2014). A high constitutive catalase activity confers resistance to methyl viologen-promoted oxidative stress in a mutant of the cyanobacterium Nostoc punctiforme ATCC 29133. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014 Jan 3.
Chen et al. (2013). Improving conversion efficiency of solar energy to electricity in cyanobacterial PEMFC by high levels of photo-H2 production. Int J of Hydrogen Energy (2013):1-8.(Anabaena, western blot).
Plominsky et al. (2013). Dinitrogen Fixation Is Restricted to the Terminal Heterocysts in the Invasive Cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii CS-505. PLOS ONE, Open Access.
Bizjak et al. (2023). Presence and activity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in Scots pine needles in a boreal forest: a nitrogen-addition experiment. Tree Physiol. 2023 Apr 18:tpad048. doi: 10.1093/treephys/tpad048. - Protocols
-
Agrisera Western Blot protocol and video tutorials
Protocols to work with plant and algal protein extractsProtein Quantitation in plant and algal samples using Agrisera global antibodies
Methodology: Plant samples are generally ground with liquid nitrogen in a mortar and pestle. The resulting powder is transferred to a plastic tube. Algal samples can be either concentrated by centrifugation or, preferably, by filtration onto glass fiber filters. Solubilization is performed in Agrisera protein extraction buffer (PEB, AS08 300) containing 0.1mg/mL PefaBloc SC (AEBSF) protease inhibitor (Roche). Disruption is most optimally obtained through flash freezing of the sample in liquid nitrogen alternated with thawing by sonication with a microtip. This process can be repeated depending on the toughness of the sample. The sample is adjusted to 50 mM dithiothreitol and heated to 70°C for 5 minutes. Samples are cooled and centrifuged briefly prior to electrophoresis.
Optimal quantitation is achieved using moderate sample loads per gel lane, generally 0.5 to 2.5 ug total protein, depending on the abundance of the target protein.
Electrophoresis and Immunoblotting: Once solubilized, the proteins can be separated electrophoretically in a number of systems. We obtain optimal results with the Invitrogen NuPAGE gel system using Bis-Tris 4-12% gradient gels. Proteins are separated in MES SDS running buffer according to the manufacturer’s recommendations at 200 V for 35 minutes. The gels are transferred to PVDF in the same apparatus, the SureLock XCell blot module, for 60 minutes at 30 V for a single gel or 80 minutes for a pair. Following transfer the blots are blocked with non-fat dry milk up to 10 % in TBS-T, for 1 h/RT with gentle agitation. The blot is incubated with primary antibody, usually at 1:25 000 to 1:50 000, for 1 h/RT (if extreme femtogram detection reagents are used) or in lower primary antibody dilution for less sensitivie reagents (mid picogram and lower).
For quantitation a relatively high primary antibody: target protein ratio gives more reliable results than immunoblots at low ratios of primary antibody:target protein.
The blot is washed extensively in TBS-T (twice briefly, once for 15 minutes and three times for five minutes). The blot is incubated with secondary antibody, for example goat anti-rabbit IgG horse radish peroxidase conjugated, AS09 602 (Agrisera), for 1h/RT. The blot is washed as above and developed with ECL detection reagents.Quantitation: When quantitated standards are included on the blot, the samples can be quantitated using the available software. Excellent quantitation can be obtained with images captured on the Bio-Rad Fluor-S-Max or equivalent instrument using Bio-Rad QuantityOne software. The contour tool is used to select the area for quantitation and the values are background subtracted to give an adjusted volume in counts for each standard and sample. Using above protocol linear standard curves are generated over 1-1.5 orders of magnitude range in target load. It is important to note that immunodetections usually show a strongly sigmoidal signal to load response curve, with a region of trace detection of low loads, a pseudolinear range and a region of saturated response with high loads. For immunoquantitation it is critical that the target proteins in the samples and the standard curve fall within the pseudolinear range. Our total detection range using this protocol spans over 2 orders of magnitude, but the quantifiable range is narrower.
References:MacKenzie et al (2005). Large reallocations of carbon, nitrogen and photosynthetic reductant among phycobilisomes, photosystems and Rubisco during light acclimation in Synechococcus elongatus are constrained in cells under low environmental inorganic carbon. Arch of Microbiol. 183: 190 - 202.
Bouchard et al. (2006) UVB effects on the photosystem II-D1 protein of phytoplankton and natural phytoplankton communities. Photochem and Photobiol 82: 936-951.
Morash et al. (2007) Macromolecular dynamics of the photosynthetic system over a seasonal developmental progression in Spartina alterniflora. Can J. of Bot. 85: 476-483(8)Application example

Total Trichodesmium sp. protein extract (lanes 6-11, 80 pmol chlorophyll loaded) extracted with PEB (AS08 300), and NifH protein standard (lanes 1-5, 0.05, 0.1, 0.3 0.75 and 1.5 pmol standard loaded) were separated on 4-12% NuPage (Invitrogen) LDS-PAGE and blotted 1h to PVDF. Blots were blocked immediately following transfer in 2% blocking reagent in 20 mM Tris, 137 mM sodium chloride pH 7.6 with 0.1% (v/v) Tween-20 (TBS-T) for 1h at room temperature with agitation. Blots were incubated in the primary antibody at a dilution of 1:40 000 for 1h at room temperature with agitation. The antibody solution was decanted and the blot was rinsed briefly twice, then washed once for 15 min and 3 times for 5 min in TBS-T at room temperature with agitation. Blots were incubated in secondary antibody (anti-hen IgY horse radish peroxidase conjugated) diluted to 1:50 000 in 2% blocking solution for 1h at room temperature with agitation. The blots were washed as above and developed for 5 min with chemiluminescent detection reagent according the manufacturers instructions. Images of the blots were obtained using a CCD imager (FluorSMax, Bio-Rad) and Quantity One software (Bio-Rad).
Recommended chemiluminescent detection reagent: AgriseraECLBright - Reviews:
-
Orly Levitan | 2009-05-13I like Agrisera product, they work well in my assay and I am planning to keep on using your products as long as my assay will require it.