1

Anti-PDC | Pyruvate decarboxylase
AS10 691 | Clonality: Polyclonal | Host: Rabbit | Reactivity: A. thaliana, O. sativa, Z. mobilis
- Product Info
-
Immunogen: KLH-conjugated peptide derived from available PDC sequences including Arabidopsis thaliana, PDC1 UniProt: O82647, TAIR: AT4G33070 and PDC2 UniProt: Q9FFT4 TAIR: AT5G54960
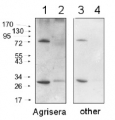
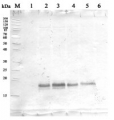
Host: Rabbit Clonality: Polyclonal Purity: Serum Format: Lyophilized Quantity: 100 µl Reconstitution: For reconstitution add 100 µl of sterile water Storage: Store lyophilized/reconstituted at -20°C; once reconstituted make aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Please remember to spin the tubes briefly prior to opening them to avoid any losses that might occur from material adhering to the cap or sides of the tube. Tested applications: Western blot (WB) Recommended dilution: 1 : 10 000 (WB) Expected | apparent MW: 65 | 65 kDa (Arabidopsis thaliana)
- Reactivity
-
Confirmed reactivity: Arabidopsis thaliana, Oryza sativa, Zymomonas mobilis Predicted reactivity: Aegilops tauschii , Brassica napus, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, Cocos nucifera, Dichanthelium oligosanthes, Fragaria ananassa, Hordeum vulgare, Glycine max, Nannochloropsis gaditana, Nicotiana tabacum, Panicum miliaceum, Phoenix dactylifera, Pisum sativum, Potamogeton distinctus, Saccharum officinarum, Solanum tuberosum, Sorghum bicolor, Ricinus communis, Rosa chinensis, Trifolium pratense, Zea mays, Vitis vinifera
Species of your interest not listed? Contact usNot reactive in: No confirmed exceptions from predicted reactivity are currently known - Application Examples
-
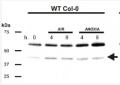
Application examples: 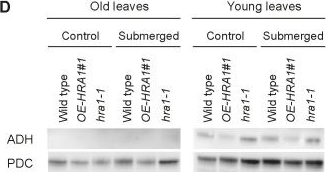
Reactant: Arabidopsis thaliana (Thale cress)
Application: Western Blotting
Pudmed ID: 25226037
Journal: PLoS Biol
Figure Number: 3D
Published Date: 2014-09-01
First Author: Giuntoli, B., Lee, S. C., et al.
Impact Factor: 7.279
Open PublicationHRA1 contributes to plant submergence survival.(A) Effect of HRA1 misexpression on rosette growth in air, or after recovery from 72 h submergence in darkness. Scale bar, 2 cm. (B) Percentage of plants surviving flooding-induced hypoxia (n?=?5), dry weight of rosette plants kept under control growth conditions (n?=?6), and dry weight of rosettes after postsubmergence recovery (n?=?6). Data are mean ± s.d.; *p<0.05, significant differences from the wild type after one-way ANOVA. (C) HRA1 regulates target gene transcripts in an age-dependent manner in leaves of plants treated with complete submergence. Transcripts were measured before submergence (“control conditions”), after 4 h submergence in darkness (“submergence”), and after 1 h de-submergence in the light (“reoxygenation”). Relative transcript values were calculated using old leaves of the wild type under control conditions as the reference sample. Data are mean ± s.d. (n?=?3); letters indicate statistically significant differences between genotypes after one-way ANOVA (p<0.05) performed independently on each leaf type. (D) Western blot analysis of ADH and PDC protein accumulation in leaves at different developmental stages from control and submerged (4 h) plants. The full-size images of the hybridized membranes can be found in Figure S10. (E) Stability of the translational fusion RAP2.12:RrLuc protein (RrLuc, Renilla reniformis luciferase) in Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts upon transfection with increasing amounts of 35S:HRA1. RAP2.12:RrLuc abundance was evaluated from the RrLuc relative activity, measured through a dual luciferase assay. Data are mean ± s.d. (n?=?4), and the asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (p<0.05) from protoplasts expressing RAP2.12:RrLuc alone, after one-way ANOVA.
- Background
-
Background: Pyruvate decarboxylase (PDC) is a homotetrameric enzyme (E.C.4.1.1.1) that catalyses the decarboxylation of pyruvic acid to acetaldehyde carbon dioxide in the cytoplasm. It is also called 2-oxo-acid carboxylase, and pyruvic decarboxylase. In anaerobic conditions, this enzyme is part of the fermentation process that occurs in yeast, especially the Saccharomyces genus, to produce ethanol by fermentation. Pyruvate decarboxylase starts this process by converting pyruvate into acetaldehyde and carbon dioxide. Pyruvate decarboxylase depends on cofactors thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) and magnesium. This enzyme should not be mistaken for the unrelated enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase, an oxidoreductase (EC 1.2.4.1), that catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA.
- Product Citations
-
Selected references: Ventura et al. (2020). Arabidopsis phenotyping reveals the importance of alcohol dehydrogenase and pyruvate decarboxylase for aerobic plant growth. Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 7;10(1):16669. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73704-x. PMID: 33028901; PMCID: PMC7542448.
Gil-Monreal et al. (2019). ERF-VII transcription factors induce ethanol fermentation in response to amino acid biosynthesis-inhibiting herbicides. J Exp Bot. 2019 Aug 6. pii: erz355. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz355.
Giuntoli et al. (2014). A trihelix DNA binding protein counterbalances hypoxia-responsive transcriptional activation in Arabidopsis. PLoS Biol. 2014 Sep 16;12(9):e1001950. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001950. eCollection 2014. - Protocols
-
Agrisera Western Blot protocol and video tutorials
Protocols to work with plant and algal protein extracts
Agrisera Educational Posters Collection - Reviews:
-
Ana Zabalza | 2020-02-17This antibody gives two bands with roots of Arabidopsis (Dilution 1:10000) and one band with Arabidopsis seedlings (Dilution 1:2500). Reactivity with seedlings published in J. Exp. Botany, 70, pp. 5839–5851.