Plant organelle/membrane isolation
- Arabidopsis lumen extraction
- Arabidopsis thylakoid extraction
- BBY preparation
- Chlorophyll measurements
- Intact chloroplast isolation method
- Mitochondrial fraction
- Nuclear fraction
- Plasma membrane fraction
- PSII RC extraction for cryo-EM
- Thylakoid extraction
- Vacuol isolation
- Collection of articles
- Diatom protein extraction
- Extraction of leaf proteins
- Phenol protein extraction
- Ponceau membrane staining
- Protein extraction from grasses
- TCA acetone precipitation method
- Western blot protocol
- Western blot video tutorial
- Western blot troubleshooting

- Western blot using IgY
- Western blot in denatured conditions (urea gel)

- Peptide neutralization/competition assay
- Quantitative Western blot
- Quantitative Western blot video tutorial
- Simultaneous Western blot
- Anti-KLH antibody removal

- Dot blot
- ELISA
- Immunohistochemistry
- Immunoprecipitation
- Immunoprecipitation/IgY
- Meiotic staining
- Yolk delipidation
Technical information
Antibody typesPurification
- Antibody purification
- Antibody purification - small amount of protein
- Elution of antibodies from affinity columns
- IgY purification methods
- Protein purification using antibodies
Protocols > Peptide neutralization/competition assayImportant noteEach antibody-antigen pair will require careful optimization of neutralization assay conditions and initial trials might not give an ultimate answer. Titration of both, antibody and free peptide needs to be done, to obtain the best result.Absorption of antibodies with the antigen can be of importance during characterization of unknown target proteins by antibodies. In some cases, it is unclear if the band seen during Western Blot detection, or the staining pattern of the tissue is the effect of a specific binding of the antibody to the target protein or due to non-specific interactions. Usually, a peptide has too low of a molecular weight to allow separation on SDS gel. It can then instead be used for a dot blot. ProcedureAbsorption of antibodies with antigen
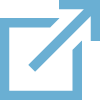
ExampleEstimation of the ratio between antibodies and a peptideAssume that IgG concentration in the serum is 10 mg/ml. Using a molecular weight of 75000 (for 1 antigen binding site), the resulting concentration will be 1.33E-7 mol/ml in stock. When using a 50 000x dilution, the concentration is 2.67E-12 mol/ml on the blot. Multiplying the antibody concentration by 100 will give you the peptide concentration that will give you a 100x excess of peptide, namely 2.67E-10 mol/ml. The molecular weight of the peptide needs to be known to complete the calculation in units of mol/ml, since you are working with an antibody concentration in mol/ml. (Peptide in mol/ml is g/ml divided by g/mol). Calculation example: PsaC peptide is 1413 g/mol. Assume the concentration is 1 mg/ml, which is therefore 7.08 E-7 mol/ml. Neutralization (competition) assayPre-incubation of antibody and peptide is done for two hours in RT in TBST, with occasional mixing. It is very important that this is done without a blocking reagent. The volume of this solution is half of that which is required for the blot (e.g., if you intend to do a 10 ml incubation with antibody, do the competition in 5 ml).The concentration of antibody in pre-incubation mixture is 2x the final concentration. The peptide-to-antibody molar ratio in this mixture should be 100:1. A control solution - TBST with just antibody at 2x final concentration - should be done. Prepare 4 % blocking solution in TBST (5 ml as in this example). At the end of the pre-incubation, add 4% blocking solution to the peptide/antibody mixture. Mix briefly and add to the blot. The final concentration of blocking reagent is now 2% and the antibody concentration is 1x the antibody dilution that is normally used. Results100x molar excess of the peptide was used in the below presented experiment (right panel, + peptide), which completely competed out the signal obtained from the target protein.
5 µg of total protein from (1) Arabidopsis thaliana leaf extracted, (2) Spinacia oleracea leaf extracted with PEB, (3) Hordeum vulgare , (4) Zea mays, extracted with Protein Extraction Buffer, PEB (AS08 300) were separated on 4-12 % NuPage (Invitrogen) LDS-PAGE and blotted 1h to PVDF. Blots were blocked immediately following transfer in 2% ECL Advance blocking reagent (GE Healthcare) in 20 mM Tris, 137 mM sodium chloride pH 7.6 with 0.1% (v/v) Tween-20 (TBS-T) for 1 h at room temperature with agitation. Blots were incubated in the primary antibody at a dilution of 1: 10 000 for 1 h at room temperature with agitation. The antibody solution was decanted and the blot was rinsed briefly twice, then washed once for 15 min and 3 times for 5 min in TBS-T at room temperature with agitation. Blots were incubated in secondary antibody (anti-rabbit IgG horse radish peroxidase conjugated, from Agrisera, AS09 602) diluted to 1:50 000 in 2% ECL Advance blocking solution for 1 h at room temperature with agitation. The blots were washed as above and developed for 5 min with ECL Advance detection reagent according to the manufacturer's instructions. Images of the blots were obtained using a CCD imager (FluorSMax, Bio-Rad) and Quantity One software (Bio-Rad). Exposure time was 30 seconds. ConclusionThe obtained band is a result of immunization with a peptide used to elicit this antibody, as it is completely depleted by antibody-peptide neutralization.
|